 The Journal of Young Pharmacists (JYP) is the official peer-reviewed journal of Phcog.Net. JYP is a leading source of information on developments and trends in pharmacy education, practice, and research. The journal publishes original research articles, reviews, case reports, editorials, and commentaries on a broad range of topics that are relevant to pharmacy students, educators, researchers and practitioners.
The Journal of Young Pharmacists (JYP) is the official peer-reviewed journal of Phcog.Net. JYP is a leading source of information on developments and trends in pharmacy education, practice, and research. The journal publishes original research articles, reviews, case reports, editorials, and commentaries on a broad range of topics that are relevant to pharmacy students, educators, researchers and practitioners.
Browse Table of Contents

Schizophrenia is a complex psychiatric disease with an unknown aetiology affecting the biological functions of the brain. It is a psychiatric condition affecting both genders irrespective of race, social class and residential status. Globally lifetime of disease is 0.4%, with a 2.5% mortality rate. Schizophrenic patients die at a young age, about 15-20 years earlier than the general population. Premature death in schizophrenic patients is mainly due to physical illness in the form of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Seventy-five percent of patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia exhibit a minimum of one physical illness and it is more complicated if symptoms are severe. Long-term drug therapy is an eminent risk factor for developing physical illnesses. There is no known cure for schizophrenia; thus, it requires lifelong treatment with antipsychotics. Second-Generation Antipsychotics (SGAs), except clozapine are the first-line drugs for treating schizophrenia. These agents are likely to develop cardiovascular and metabolic side effects like hypertension, hyperlipidemia, weight gain, diabetes mellitus and obesity. Another contributing factor is a sedentary lifestyle. Ignoring these factors while undergoing treatment may result in increased burden, decreased quality of life and shorter life expectancy. Clinical pharmacists have a vital role in managing these patients through proper counselling and medication monitoring for better control of the illness.

Osteoporosis diagnosis relies primarily on a clinical assessment involving the observation of signs and symptoms. The origins of this disorder may be either causative or risk-related, with some factors being preventable while others are not. Treatment modalities are diverse, constantly under study for improved outcomes and aimed at minimizing adverse effects from various therapeutic approaches.This study aims to comprehensively explorethe etiology, pathophysiology and advancements in osteoporosis management. A thorough review was conducted, utilizing an extensive search of MEDLINE, PubMed and EMBASE databases spanning from January 1987 to March 2023. The search terms included “osteoporosis,” “etiology of osteoporosis,” “pathophysiology,” “clinical features,” and “treatment of osteoporosis.” The osteoporosis treatment mainly combinations with or without drug therapy and ensure the sufficient intake of the calcium ion and assess the levels of vitamin D. diminish the polypharmacy, particularly with tranquilizer. Bisphosphonates are the main medicament for the treatment of osteoporosis but should be taken separately from food due to poor absorption. Recent years have witnessed the emergence of numerous treatment options, including novel drugs and their combinations with or without non-pharmacological therapies, demonstrating promising results. Further research is imperative to implement advanced regimens for the treatment of osteoporosis.

Several studies have established that diabetes can exacerbate the neurodegeneration process. Some studies have reported the potential use of medicinal plants to inhibit neurodegenerative activities in diabetes. Therefore, this systematic review aims to evaluate the potential of medicinal plants to ameliorate neurodegenerative activities in diabetes. This systematic review was reported according to PRISMA guidelines. A systematic search was performed in four databases which were PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar and Science Direct. Seven articles that fulfilled the inclusion criteria were selected for reporting this review. The medicinal plants reported in these articles were studied for their blood glucose lowering effect, acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and cognitive improvement ability through a behavioural test known as the Morris water maze. The medicinal plants such as Liuwei Dihuang Decoction (LWDHD), Flos Puerariae Extract (FPE), methanolic leaf extract of Peristrophe bicalyculata (MEPb), Ethanol Extract of Clitorea ternatea (EECT), Lychee Seed Extract (LSE) Andrographis paniculata extract (AP), andrographolide and Petroleum Ether Extract of Carica papaya Seeds (PEECPS) have shown significant result in Morris water maze test and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, suggesting their ability to improve cognitive behaviour. They were also reported to have blood glucose lowering effect except for MEPb. LWDHD, FPE, MEPb, EECT, LSE, AP, andrographolide and PEECPS reported in these articles have shown potential in improving cognitive behaviour of diabetic animals. They were also reported to have anti-diabetic effects except for MEPb. However, more studies and research should be conducted to ensure the potential and safe use of these medicinal plants.

Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is one of the most common diabetic complications which can lead to vision loss if left unattended. Medicinal plants are considered as a treatment option for its lesser side effects. Given the overwhelming number of studies on various medicinal plants using different subjects, this systematic review aims to update the current status of the potential of medicinal plants in ameliorating DR. Literature from the years 2011 to 2020 was retrieved from PubMed, ScienceDirect and Scopus databases using the search terms: Medicinal plants AND (diabetes OR hyper glycaemia) AND retinopathy. The PRISMA guidelines were adhered to for reporting the systematic review, while the SYRCLE tool was used to assess the risk of bias in animal studies. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were established for selecting compatible studies. Based on these criteria, four out of 439 studies were selected: Studies on DR in rats included three or more assays for measuring retinal vascular permeability, VEGF protein and gene expressions and body weight. An additional six studies from a manual search brought the total to ten selected studies. All studied medicinal plants demonstrated potential in ameliorating DR, based on their downregulation of diabetes-induced retinal vascular leakage and VEGF expressions. Medicinal plants with significant potential in attenuating DR included Zingiberzerumbet rhizomes and its active ingredient, zerumbone; Lycium barbarum; Plantaginis semen; and apocynin. The aqueous extracts of Radix astragali, Radix angelica sinensis, Panax notoginseng, Lycopus lucidus Turcz and total lignans from Fructus arctii can be further evaluated in future studies.

This review explores the diverse properties and applications of Annona muricata, referred to as soursop or graviola. The historical significance of medicinal herbs, particularly Annona muricata, was used in ancient medical practices which produce a variety of chemical compounds, including those of defense mechanisms against pests, diseases, fungi and herbivorous mammals. One of the key highlights of A. muricata is its role as a rich source of essential nutrients, including metals that play pivotal roles as cofactors in biochemical processes. This plant has garnered attention for its therapeutic properties in traditional medicine to address many maladies. A. muricata’s medicinal properties include treating fever, acne, insomnia, hypertension, respiratory disorders, parasitic and bacterial infections, inflammation, diabetes and cancer. This review explores the scientific basis behind these traditional uses, focusing on the biochemical mechanisms that underlie A. muricata’s therapeutic. Furthermore, this review discusses the global prevalence of A. muricata, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions and its adaptation to diverse environmental conditions, highlighting its promising role in addressing contemporary health challenges.

The field of ufasomes has great promise for revolutionizing drug delivery. Ufasomes have the potential to overcome limitations, enhance medicine and therapy and pave the way for future pharmacological formulations that are more effective and patient-friendly with more research and development. Ufasomes are suspensions of a closed lipid bilayer made up of fatty acids and their ionized species. They are unsaturated fatty acid vesicles with a pH range of 7-9. The primary benefit of ufasomes is that they are mostly composed of fatty acids, which allow them to readily permeate skin and exhibit systemic activity. Ufasomes demonstrate specific medication delivery. There are several kinds of preparation techniques, including vortex mixing, the autopoietic process, the round bottom flask method and thin film layer hydration. Alcohol and cholesterol are added during the preparation of ufasomes. The paper examines ufasome characteristics, pharmacokinetics, uses, advantages, disadvantages and applications. These vesicles have uses in nutrition encapsulation, drug delivery and cosmetic development.

Atherosclerosis is a primary factor in many cardiovascular diseases. Current treatments lack effectiveness in reducing the risk and progression of the disease, highlighting the need for better preventive measures. Precision medicine in cardiology offers personalized and patient-centered approaches to disease prevention and treatment. Innovations like machine learning and AI-assisted therapies are being explored to combat atherosclerosis, drawing from network medicine principles. This personalized approach involves analyzing gene regulation, metabolic pathways and protein interactions through mRNA therapeutics and immunomodulation techniques. Precision medicine shows promise in cardiovascular pharmacology by enabling targeted drug delivery and minimizing side effects. The review discusses AI-assisted drug discovery tools for individualized therapy and future prospects in nucleic acid-based treatments like antisense oligonucleotide therapeutics, aptamer therapy, siRNA-mediated treatments and gene slicing in precision medicine.

Diabetic neuropathy is a prevalent and painful condition impacting the nervous system and a common clinical consequence of Diabetes Mellitus (DM). Effective management of various forms of Diabetic Neuropathy (DN), such as peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, proximal neuropathy and mononeuropathy, remains challenging. Management of blood glucose levels in diabetic patients may delay the onset of diabetic neuropathic conditions. Recently, considerable research on natural products, including isolating bioactive phytochemicals from plants and investigating their potential impact on DN, is underway. Flavonoids are abundant secondary metabolites in plants and this review primarily focuses on the possible applications of key flavonoids (such as quercetin, rutin, catechin, diosmin, kaempferol and naringin) for preventing and treating DN. In recent times, herbal medicine, especially flavonoids for treating pain, inflammation, DM and other conditions, has been investigated thoroughly to develop them as promising candidates for DN. This paper discusses the probable mechanism of action of flavonoids against DN. Clinical and pharmaceutical challenges for the management of DN and developing flavonoids as drug molecules targeting DN are also highlighted.

Thiazide Induced Hyponatremia (TIH) is one of the main causes of fatal hyponatremia among elderly. The global and Indian prevalence ranges from 4-14% and 30%, respectively. This paper reviewed the clinical implications of thiazide usage and its side effect especially hyponatremia from the global and Indian perspective. A literature review was performed using databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar between January and May, 2023. This review deals with prevalence, mechanism of TIH development, risk factor, signs and symptoms, mortality, treatment modalities of hyponatremia, pharmacist roles and prevention. Advancing age, female gender, alcohol consumption, low body mass index, several medications such as antidepressants, antiepileptics, corticosteroid withdrawal, hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide, etc., are also the risk factor for TIH. The signs and symptoms include headache, lethargy, mental confusion, etc., The mortality rate in India varies from 7-51%. The management is influenced by the presence or absence of neurologic symptoms. Treatment involves stopping thiazides, maintaining a regular diet (especially K+ supplements), limiting water intake, furosemide administration and administering isotonic saline or hypertonic saline in case of severe hyponatremia. Clinical pharmacists have an important role in identifying and managing TIH. Early diagnosis, better management and prevention strategies improve the quality of life among elderly.

Vascular endothelial growth factor i.e., VEGF inhibitor, Ranibizumab (RNZB) has altered ophthalmology as it is providing a treatment option for a range of retinal disorders. The pharmacological attributes of RNZB in relation to ophthalmic applications are explored in this work. It explores its present applications for diseases like diabetic retinal disease along with age-related macular degeneration. The dissertation also addresses current studies on RNZB’s potential to treat additional ocular conditions. Through an analysis of both well-established uses and intriguing novel avenues, this study offers a thorough grasp of RNZB’s current and potential future roles in ophthalmology. Furthermore, we investigate new developments and potential paths in the creation of innovative formulations, combination treatments, and targeted drug delivery systems with the goal of improving the effectiveness and long-term viability of RNZB therapy. Through the integration of current and future perspectives, this study aims to outline a path forward for optimising RNZB’s therapeutic value, ultimately enhancing the paradigm for managing ocular illnesses that pose a threat to vision. Researchers offer a thorough summary of the molecular pathways that RNZB targets and its effects on pathological angiogenesis, vascular permeability, and the resolution of macular edoema by synthesising the available data.

The traditional preventive method for treating decay often entails resin-based sealants, topical fluoride application and Glass Ionomer based sealants (GIC sealants). At present, topical fluoride application is less effective when compared with the pit and fissure sealant, as resin sealants were mentioned to be efficient in preventing occlusal cavities in both primary and permanent teeth by formation of resin tags. However, moisture contamination is a more common problem encountered with hydrophobic sealants, but not with GIC sealants, as they are not as moisture sensitive as hydrophobic resins. Hence, hydrophilic sealants were developed. Therefore, this current systematic review evaluated the current literature on the efficacy of caries prevention and retention between moisture-tolerant resin and GIC -based sealants among children and adolescents aged 6-18 years. Clinical trials assessing the effectiveness of Moisture Tolerant resin and GIC based sealant among 6-18 years of age groups, the follow-up duration exceedingly over 6 months were added. Two reviewers (J;JJ) extracted data data separately from the included publications, which they then integrated. Cochrane risk of assessment tool {RoB2} was used to evaluate the study's quality. Following six and twelve months, there was statistical significance in the caries prevention and retention of moisture tolerant resin-based sealants over GIC based sealants. The retention of moisture-tolerant sealants was statistically significant in all five of the selected experiments when compared to GIC sealants, showing the effectiveness of moisture-tolerant sealants in terms of retention.
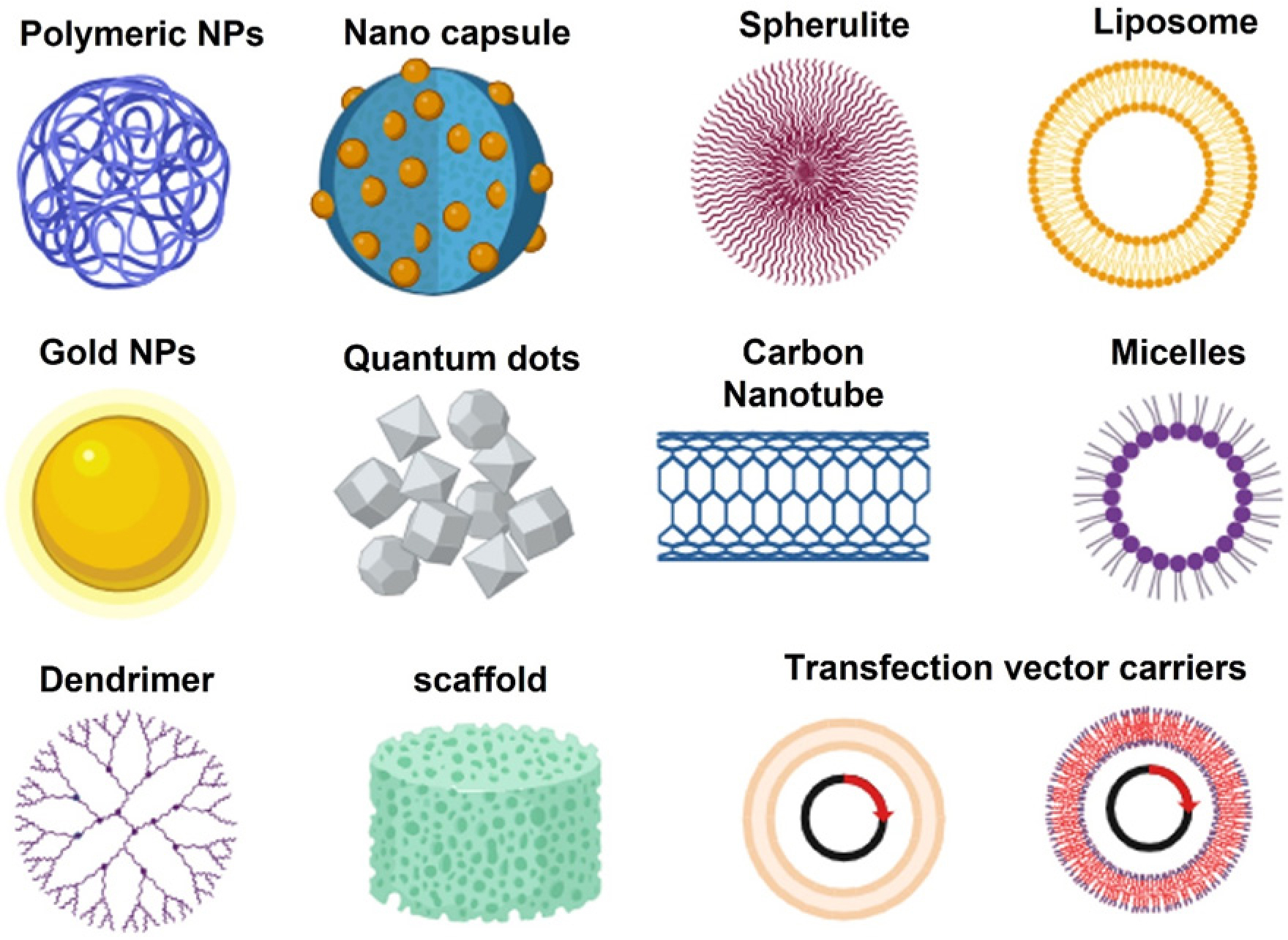
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is still one of the most aggressive and resistant brain tumours, and current treatment options provide only minimal improvements in survival. Effective drug delivery is severely hampered by the complexity of GBM, which is defined by its heterogeneity and the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB). The most recent developments in precision drug delivery technology are examined in this study to address these issues and enhance treatment outcomes for GBM patients. We discuss various innovative approaches, including nanoparticle-based systems, bioconjugates, ligand-targeted therapies, and gene delivery platforms. These technologies are specifically engineered to enhance drug penetration across the BBB, target tumour-specific pathways, and minimise off-target effects, thereby potentially revolutionizing GBM treatment. The review also addresses the challenges associated with clinical translation, including regulatory hurdles, safety concerns, and the need for scalable manufacturing processes. This review endeavours to offer a comprehensive overview of the potential of precision drug delivery to facilitate more personalised and effective GBM therapies in the near future by emphasising the most promising strategies and emergent trends in the field.

Background:
In the conventional Indian medical system, Cupressus sempervirens L., a member of the Cupressaceae family, is highly significant. C. sempervirens is a traditional medicinal plant; has been reported in the literature that the dried leaves are used as a contraceptive and to treat inflammation, diabetes, stomach pain, toothaches, and laryngitis. Hence, the present study is planned to evaluate antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and protective effect of C. sempervirens leaves extract in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.
Materials and Methods:
The HPLC analysis of the ethanolic plant extract was followed by an in vivo antidiabetic activity. In order to evaluate antidiabetic measures such as body weight, urine volume, blood glucose level, total cholesterol, triglyceride, and lipid profile as antihypertensive parameters, the Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes mellitus in a rat model is being investigated for in vivo activity.
Results:
The presence of phenolic acid, alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, terpenoid, and steroids was identified by HPLC analysis of the ethanol extract. Gallic and tannic acids were identified in the phenolic components. The animals in each group having received samples were observed on days 1, 5, 10, 15, and 20, and several parameters were assessed. A significant effect is observed within the group of ethanolic extract. According to histopathological study of pancreatic and liver tissue, the damaged structure of the pancreas and liver was improved by treatment with a larger dose of ethanolic extract.
Conclusion:
Scientific evidence for their use in antidiabetic therapy is provided by the ethanolic extract, which produced a significant antidiabetic effect.

Background:
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) presents a significant clinical challenge due to its aggressive nature and limited therapeutic options. A promising treatment strategy involves targeting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) signaling and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways that are hyperactivated in many breast carcinomas. In our study, we aimed to develop a drug delivery system utilizing Paclitaxel (PTX) bio-conjugated with mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) small interfering RNA (siRNA) nanoparticles, which were further conjugated with EGFR to specifically target TNBC cells.
Materials and Methods:
The nanoparticles were synthesized using a precipitation method followed by solvent evaporation. They were characterized for size, shape, entrapment efficiency, and drug release kinetics. Additionally, we assessed their cytotoxicity, migration assay, and siRNA binding efficiency using gel retardation.
Results:
The results showed that the EGFR-mTOR siRNA-loaded immuno nanoparticles had a mean size of 186.6 nm with a zeta potential of 46.57±12.3 mV and an entrapment efficiency of 76.3±3.6%. Gel retardation assays confirmed the integrity of mTOR post-conjugation with mTOR immuno nanoparticles. The anticancer activity of mTOR immuno nanoparticles was evaluated using MDA-MB231 and MDA-MB468 TNBC cell lines, demonstrating significant cytotoxicity. The antibody-conjugated immuno nanoparticles showed enhanced targeting specificity and efficacy against TNBC cells.
Conclusion:
In summary, mTOR immuno nanoparticles exhibit potential as a targeted therapeutic strategy for TNBC, providing enhanced effectiveness while reducing the adverse effects associated with conventional chemotherapy. This novel drug delivery system's potential to improve therapeutic efficacy and mitigate systemic toxicity underscores its translational relevance in cancer treatment.

Background
Quinazolinone compounds are a preferred class of multi-agent therapeutics in the domains of biology and pharmacology. One of this scaffold's most notable biological functions is its anticancer properties. Numerous well-known quinazolines with anticancer properties operate on diverse molecular targets via distinct methods. Hence, the present study is planned to design the new series of substituted Quinazolinone derivatives and synthesize, carry out molecular docking studies for the proposed compounds against EGFR TK-PDB: 1M17 and CDK-PDB: 2KW6 receptor by using PyRx virtual screening tools Auto-dock vina software 0.9 version and to screen the compounds for their in vitro cytotoxicity against MCF-7 breast cancer cell line.
Materials and Methods
A unique set of compounds, dihydro-quinazolinone QS1-QS4, and its scaffold, were created. Recrystallization by ethanol purifies every produced chemical. The protein was downloaded from PDB and Auto-dock vina PyRx (0.8) was used to predict it in silico studies.
Results
TLC and IR are used to describe each derivative. The produced compounds were tested for their ability to inhibit cancer in vitro using the MCF7 cancer cell line and reference medication doxorubicin. The results of the molecular docking study indicated that the synthesized compounds had a good binding affinity for the 1M17 and 2KW6 macromolecules.
Conclusion
The MTT assay was used to screen the synthesized compounds based on docking score and assess their anticancer activities in vitro. The molecule that was produced and evaluated showed increased activity and was also screened for in vitro cytotoxicity against the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line, which results in concentration rises and decreases in cell viability.

Background
Tuberculosis (TB) is a leading airborne disease, impacting millions annually and ranking among the top ten causes of global mortality. Post-COVID-19, TB incidence has increased due to its pulmonary nature, which facilitates infection spread. Current TB treatments primarily control rather than prevent infection and are associated with mycobacterial resistance and significant side effects.
Purpose
This study aims to design and evaluate thiophene based Schiff bases as potential antitubercular agents targeting polyketide synthase 13 (Pks 13), crucial for mycolic acid production and less prone to resistance.
Materials and Methods
Thiophene-based Schiff bases were designed based on Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) analysis and subjected to in silico approaches, including molecular docking against Pks 13. Compounds with the best docking scores underwent further in silico analysis (ADME, drug-likeness, toxicity). These compounds were synthesized, recrystallized, characterized and evaluated for in vitro antitubercular activity using the Microplate Alamar Blue Assay (MABA).
Results
Compounds Ca3 and Ca5 had the best docking scores (-8.6 and -8.4 kcal/mol) and showed significant antitubercular activity in vitro at 25 μg/mL and 12 μg/mL, respectively. In silico and in vitro results correlated well, indicating strong binding affinity and potency against Pks 13.
Conclusion
Compounds Ca3 and Ca5 show promise as potent antitubercular agents targeting polyketide synthase 13, supporting further development and optimization of thiophene-based Schiff bases for TB treatment.

Background
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a debilitating viral infection that compromises the immune system, rendering individuals vulnerable to opportunistic infections. While antiretroviral therapy can effectively manage the condition, the development of novel treatment strategies remains crucial. This study aims to create and validate a robust reversed-phase HPLC routine for the concurrent quantification of lenacapavir and bictegravir, two antiretroviral agents.
Materials and Methods
A novel chromatographic separation method was developed utilizing a Hypersil ODS C18 column (4.6x250 mm, 5 μm particle size). The mobile phase, a gradient mixture of 0.1% OPA buffer and acetonitrile, was optimized for efficient analyte elution. Chromatographic detection was performed at 220 nm with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute, injecting 20 μL of sample volume for each analysis.
Results
Linearity for lenacapavir was established across a concentration range of 72-216 μg/mL, while bictegravir demonstrated linearity from 24-72 μg/mL. The chromatographic retention times for lenacapavir and bictegravir were computed to be 2.17 and 11.46 min, respectively. Recovery studies indicated that both analytes could be accurately quantified, with recovery percentages falling within the 98-102% range.
Conclusion
In accordance with ICH requirements, the novel approach was successfully validated. The devised method is dependable and cost-effective for routine analysis with respect to all parameters that have been evaluated.

Background
Remdesivir is a antiviral drug, which has approved in COVID-19 pandemic as emergency use. In order to solubilize the remdesivir in injection form, Sulfobutylether-Beta-Cyclodextrin (SBECD) is used as solubility enhancer. Since SBECB is excreted by the kidney and it is contradicted for patients with severe renal impairment.
Objectives
This research aim to formulate and evaluate the dry powder inhaler formulation of remdesivir mucoadhesive nanoparticle for respiratory diseases.
Materials and Methods
The nanoparticle was prepared by nanoprecipitation method using PLGA and Chitosan, the prepared nanoparticle was subjeted to various studies include physiochemical characterization, mucoadhesive properties. The formulation has loaded in Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI) and evaluated its dispensing properties.
Results
The prepared nanoparticle has spherical shape with 104.6 nm in size and zeta potential of -12.7 mV. The nanoparticle has 72.06% of entrapment efficiency with significant in sustained drug release of 85.1% at 48 hr. The mucoadhesive nanoparticle showed negligible damage in epithelial integrity with DPI emitted dose of 87.02% and MMAD of 2.90 μm. The prepared nanoparticle showed significant mucoadhesive strength of 77.1% with lungs mucosa.
Conclusion
Based on the above studies, remdesivir mucoadhesive nanoparticle deliver through DPI, it could be the best alternative route of administration during emergency situation.

Background
Fast Disintegrating Tablets (FDTs) are crucial in pharmaceuticals for rapid drug onset and improved patient compliance, particularly for those who have difficulty swallowing. Chlorpheniramine Maleate (CPM), an antihistamine used for allergy relief, is the focus of this study to develop FDTs. The rapid onset of action is advantageous in treating allergic reactions, providing quick relief from symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itching. By exploring this innovative approach, the present study aims to enhance the convenience, effectiveness, and patient acceptance of oral drug delivery.
Materials and Methods
Tablets were formulated by direct compression, incorporating three superdisintegrants: Tulasi powder, Isabgol mucilage, and Croscarmellose sodium. Various pre- and post-compression parameters were examined, including flow properties, hardness, wetting time, water absorption ratio, disintegration time, in-vitro dissolution studies, and accelerated stability studies.
Results
Pre-compression parameters showed good compressibility and flow properties. Post-compression parameters met specified limits, with formulation F6, containing 14 mg Isabgol mucilage, demonstrating the lowest disintegration time (7 sec) and highest cumulative drug release (98.85%). Accelerated stability testing confirmed the stability of formulation F6 over three months under elevated temperature and humidity conditions.
Conclusion
Isabgol mucilage proved to be the optimal superdisintegrant, exhibiting the fastest disintegration time, highest drug release, and favorable flow properties offering a reliable solution for patients with swallowing difficulties and ensuring rapid relief. This study highlights the potential of Isabgol mucilage in enhancing the performance of FDTs, paving the way for improved patient outcomes and compliance.

Background
Nebivolol hydrochloride is a beta blocker used to treat hypertension but has low oral bioavailability (12%) because of first-pass metabolism by CYP3A enzymes. Hence to improve bioavailability, nebivolol hydrochloride loaded transferosomes delivery via transdermal route is studied.
Materials and Methods
Transferosomes were developed by thin film hydration method and evaluated for physicochemical properties. Study state flux was determined by permeability studies on excised rat abdominal skin using Franz diffusion cells. To evaluate the efficacy of transferosomes Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic studies were carried out on Wistar male rats.
Results
Optimized transferosomal formulation TF2D comprises soya lecithin, tween80 and drug in the proportion 90:10:5 with 5% DMSO as permeation enhancer. The optimized formulation showed vesicle size 141.9 nm, PDI 0.143, Zeta potential -39.1 mV, entrapment efficiency 98.5% and steady state flux 97.4 μg/cm2/hr. The steady state flux of the TF2D was 4.23 times the flux of drug suspension. Scanning electron microscopic images displayed sphere shaped vesicles. FTIR studies confirm the compatibility between drug and formulation additives. Antihypertensive activity of TF2D was significantly high compared to oral drug suspension and the effect was sustained up to 48 hr. The bioavailability of TF2D was significantly high at p<0.0001 (4.13 folds) in comparison with oral drug suspension. The histopathological study on the rat skin confirmed the safety of the transferosomal formulation of nebivolol.
Conclusion
We conclude that introducing transferosomes as vesicular drug carriers via transdermal route could significantly enhance the bioavailability of nebivolol hydrochloride.

Background
Proton pump inhibitors are used for suppressing gastric acid secretion. They are among the most routinely prescribed drugs globally due to their excellent efficacy and low risk of side effects, yet they are frequently used inappropriately. Although extensive studies are available in Western countries on proton pump inhibitor appropriateness, such data from India is still very limited.
Materials and Methods
This is a hospital-based cross-sectional study where 402 patients participated, and appropriateness was assessed using standard guidelines (Food and Drug Administration, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, and American College of Gastroenterology) and the Medication Appropriateness Index tool (among proton pump inhibitor users).
Results
Logistic regression was performed, and strong relationships between the appropriateness of proton pump inhibitor usage and gender and comorbidity were observed. According to standard guidelines, appropriate usage of proton pump inhibitors was recorded as highest during hospitalization (33%), and least during discharge (8%).
Conclusion
This study explored the appropriateness of proton pump inhibitor prescriptions among general medicine inpatients at a secondary care referral hospital in Andhra Pradesh. Inappropriate proton pump inhibitor usage is still more prevalent in our country, and it is imperative to enhance appropriate proton pump inhibitor prescription, particularly with regard to minimizing misuse, to attain a noteworthy reduction in healthcare expenses and anticipate a decreased occurrence of possible unfavorable outcomes.

Background
Many women experience sexual disorders or side effects due to factors such as age or medication use. The most common issues are lack of desire and inability to become aroused during sex. Women are more likely than men to suffer from sexual inefficiency, with a prevalence of 43% compared to 31% for men. This study aims to determine the prevalence and compare the types of sexual side effects of psychotropic medications in female psychiatric patients, while exploring the impact of socio-demographic factors and potential correlation with menstruation.
Materials and Methods
An observational, prospective cross-sectional study was conducted on patients at the psychological medicine department of Dhiraj Hospital, SVDU. Patients with a history of psychiatric illness or those taking psychedelic medication for at least a month were included based on study criteria. The Female Sexual Function Index Scale was used, consisting of 19 questions divided into six domains representing sexual side effects in female patients: Desire, Arousal, Lubrication, Orgasm, Satisfaction, and Pain. Patient responses were collected and interpreted using the FSFI score to determine the final score.
Results
According to the study, the prevalence of sexual problems varies among patients. Out of the population studied, 103 patients experienced desire problems, which accounts for 51.73% of the group. Arousal problems affected 110 patients, representing 55.23% of the population. Lubrication issues were reported by 138 patients, which represent a prevalence of 69.19%. The prevalence of orgasm problems was 62.25%, affecting 124 patients. A total of 164 patients suffered from satisfaction problems, resulting in a prevalence rate of 82.33%. In contrast, 120 patients reported pain, equating to a prevalence of 60.28%. Finally, the study found that 128 patients had a full score, which accounts for a prevalence rate of 64.26%.
Conclusion
In summary, it is crucial to understand the sexual side effects that may arise due to psychotropic medication in women. This study highlights the prevalence of such side effects and the importance of addressing them to prevent additional stress on patients’ mental health. Recognizing and discussing these potential side effects with healthcare providers can lead to better management of psychiatric conditions and improve the overall well-being of patients.

Introduction
Globally, one in 10 adults is living with diabetes and nearly 40% remain undiagnosed making it a silent killer. India’s traditional medical system, Ayurveda, has been practiced for thousands of years. As the treatment of Ayurveda has a high acceptability in the Indian subcontinent, it is commonly used for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The present study is planned to identify and explore the variables related to glycemic control in T2DM patients receiving Ayurvedic treatment.
Materials and Methods
A total of 100 subjects were studied in cross-section taking into consideration the inclusion and exclusion criteria and selected through convenience sampling. Study subjects included patients of T2DM on Ayurveda therapy irrespective of their duration of therapy and disease. Ethical permission was taken and data collected after due consent from the study subjects.
Results
About 40% of the patients did have a family history of T2DM with a first-degree relative. The mean age of diagnosis was early with the history of two or more affected family members. A significant association was observed between gender and glycemic levels. Age and duration of illness also had a significant association with HbA1c levels among the subjects.
Conclusion
It can be concluded from the study that the key features associated with diabetic control among patients on Ayurveda therapy are mainly the family history, age at diagnosis and thereby the duration of illness, current age and gender of subjects.

Background
The present research examines how prepared healthcare and non-healthcare professionals are to deal with the next wave of the COVID 19 pandemic outbreak and what we can take away from previous outbreaks of the pandemic.
Materials and Methods
Using a World Health Organization (WHO) Survey Tool and Guidance for Monitoring Knowledge, Risk Perception, Preventive Behaviour and Trust to Inform Pandemic Outbreak Response, a web-based cross-sectional survey was carried out among healthcare and non-healthcare workers from May to July 2022 (three months). SPSS 26.0 was used to analyse the data.
Results
A total of 432 participants gave their consent to participate in the study. Of these, 202 (46.8%) men, 225 (52.1%) women and 5 (1.2%) preferred not to disclose. 95% of the participants were younger than the age range of 18 to 25 and 307 (71.1%) of the participants were healthcare workers. The majority of the study participants believed they had a lower chance of contracting COVID-19. Half of the participants indicated they were able to fight against COVID-19 through their actions and self-precautions, whereas 36% of participants said that it’s extremely difficult for them to stay away from COVID-19.
Conclusion
Participants are well-informed about COVID-19 and well-prepared for the next wave of COVID-19. However, few participants do not follow the preventive steps to protect themselves from the infection. Maintaining high vaccination rates, practicing effective public health measures such as mask-wearing and physical distancing, implementing robust testing and contact tracing systems and prioritizing early detection and containment of emerging variants are crucial steps to prevent from next wave of the Pandemic.

Background
Vaccine hesitancy refers to the reluctance or outright refusal to be immunized despite vaccine availability. It spans from full acceptance to complete rejection of all vaccines, with most hesitancy instances lying in between. Factors influencing vaccine hesitancy encompass confidence (trust in vaccines, delivery systems and providers), convenience (accessibility of immunization services), complacency (perceived lack of necessity or value for vaccines), skepticism (influenced by knowledge and information) and psychological elements like conspiratorial thinking. This comprehension is crucial for effectively addressing vaccine hesitancy. The study aimed to determine predictors linked to vaccine hesitancy within the studied population.
Materials and Methods
Employing a cross-sectional survey design, the investigator acquired foundational knowledge through various courses on vaccine safety, biology, hesitancy and anti-vaccination beliefs. Participants, consenting adults from Mysore city visiting JSS Hospital for any reason, underwent purposeful sampling based on specific eligibility criteria.
Results
The study included a diverse group, with the female population comprising 59.87%. Demographics, such as age and socio-economic status, were also examined. Statistical analysis utilized SPSS software and data presentation involved mean, standard deviation, percentages and visual representations. The study identified a vaccine hesitancy prevalence of 23.12%, with males and the age group of 40-49 years showing higher likelihoods of hesitancy.
Conclusion
By scrutinizing a subgroup, researchers gleaned insights into factors fueling hesitancy, paving the way for targeted interventions and strategies to foster vaccine acceptance and uptake.

Background
Cancer patients’ Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL) could be substantially impaired by Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN). Hence, the present study is aimed to assess the prevalence of CIPN and its influence on HRQOL among various cancer patients.
Materials and Methods
The study was a prospective observational cross-sectional study conducted in the Department of Medical Oncology, Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research (DU) from Jan 2023 to July 2023. A total of 125 patients treated with various chemotherapeutic drugs were included as per inclusion and exclusion criteria. Patients were evaluated for CIPN using a validated Self-Administered Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs (SLANSS) questionnaire and the health-related quality of life was evaluated by using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (EORTC-CIPN20) questionnaire.
Results
The prevalence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy was found to be 12%. Patients receiving chemotherapy experienced a significantly higher number of peripheral neuropathy-related complaints (p<0.001). Overall, the patients expressed that peripheral neuropathy had a detrimental impact on their quality of life, particularly with sensory and motor functions.
Conclusion
Chemotherapeutic drug has the potential to cause the adverse effect of peripheral neuropathy. Particularly, antimetabolites and platinum derivative combination had reported a higher incidence of peripheral neuropathy (94.7%). Consequently, it has a detrimental impact on the health-related quality of life among cancer patients.

Background
Breast cancer remains a significant global health concern and radiation therapy plays a vital role in reducing disease-related mortality and recurrence rates. However, Radiation Dermatitis (RD) is a common adverse effect experienced by breast cancer patients undergoing Radiation Therapy (RT). This study assessed the prevalence of acute radiation dermatitis and its influencing factors in breast cancer patients receiving radiation therapy and observed the response to treatment for acute radiation dermatitis.
Materials and Methods
A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted in the Department of Radiation Oncology, Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research (DU). A total of 87 patients were recruited for the study, of which 51 patients developed radiation dermatitis.
Results
Nearly, 58.6% of the breast cancer patients who received radiation therapy developed radiation dermatitis. The majority of the patients had Grade 3 radiation dermatitis. Radiation dermatitis was completely healed for the majority of patients. Influencing factors like type of clothing, texture of cloth, use of lukewarm water, soft soap, bed sheets, electric razor and avoidance of heating pads/ice packs were improved after counseling and distribution of patient information leaflet.
Conclusion
Among various grades of acute radiation dermatitis, majority of the patients (44.82%) had grade 3 radiation dermatitis. The counseling sessions appear to have influenced various factors related to clothing and skincare. Influencing factors like type of clothing, texture of cloth, use of lukewarm water, soft soap, bed sheets, electric razor and avoidance of heating pads/ice packs were improved after providing counseling and distribution of patient information leaflet.

Background
Drug usage studies and prescription pattern monitoring in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) play a pivotal role in optimizing patient care, ensuring safety, managing resources effectively, improving quality, and advancing medical knowledge and practice. The purpose of the study was to generate data on drug utilization patterns and determine the rationality of prescriptions using WHO core indicators.
Materials and Methods
A record-based, cross-sectional, observational study was carried out at the ICU of Shraddha Hospital, Borsad, Gujarat. The demographics of the patients, drug usage patterns, and Defined Daily Dose (DDD)/100-bed days of frequently utilized medication in the ICU department were investigated.
Results
A total of 178 patients were analyzed, with a mean age of 52.06±17.5 years and male predominance (67%). The most common concurrent illnesses were hypertension and diabetes mellitus. A total of 2,352 prescription drugs have been prescribed. The mean number of drugs for each prescription seemed to be 13.21±5. Parenteral administration was the most used route, accounting for 61.18%. Ondansetron was the most prescribed medication, followed by pantoprazole, furosemide, ceftriaxone, budesonide, and aspirin.
Conclusion
There were too many prescription drugs prescribed for each patient on average; however, polypharmacy may be unavoidable during the patient’s stay in the intensive care unit due to various illnesses. Improving prescribing trends involves reducing the quantity of drugs per prescription and emphasizing the use of generic medications. This approach not only enhances the efficacy of prescriptions but also alleviates the financial burden on patients.

Background:
More than the newly diagnosed COVID-19, healthcare systems are increasingly dealing with the complex long-term health consequences of individuals who have not entirely recovered from the SARS-CoV-2 infection. This study aimed to assess the prevalence of long-term COVID and the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on this prevalence and health-related quality of life during recovery.
Materials and Methods:
A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted with 624 individuals who had recovered from COVID-19. Demographic information, vaccination status, Long-COVID symptoms, and health-related quality of life were collected. Follow-up assessments were conducted at 6-month and 12-month intervals.
Results:
The prevalence of ongoing symptomatic COVID-19 manifestations was 87.3%. Cough was the most frequently reported complaint, affecting 64.3% of the participants. The prevalence of post-COVID syndrome decreased to 72.1% at 6 months and remained at 73.9% at 12 months, with fatigue (18.6%) and headaches (20.8%) being the most frequently reported symptoms, respectively. At one month, six months, and twelve months after COVID-19 recovery, the average health-related quality of life for individuals was measured to be 0.90 ± 0.13, 0.93 ± 0.11, and 0.94 ± 0.1, respectively. Long-COVID were more prevalent in vaccinated individuals (74.5%) compared to non-vaccinated (69.6%). The health-related quality of life was significantly lower in those who had received the COVID-19 vaccine compared to unvaccinated individuals (0.94 ± 0.1 vs. 0.96 ± 0.07).
Conclusion:
Long-term COVID symptoms decreased, and health-related quality of life improved during recovery. However, COVID-19 vaccination was associated with increased Long-term COVID prevalence and lower health-related quality of life.

Background
Antimicrobial stewardship is referred as a concerted endeavor to ensure proper usage of antibiotics and deviations in programme leads to inappropriate use of antimicrobials, hence it requires standard tool to evaluate usage and measure improvement by alleviating deviations. The objective of the study is to observe antimicrobial stewardship activities in surgical patients and to develop comparison between antimicrobial recommending techniques with standard guideline available within hospital. To identify suitable variables or factors to measure antimicrobial stewardship and thereby accomplish recommendations for rational use of antimicrobials.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted in the department of orthopedics and plastic surgery, in a major trauma care centre in Tamil Nadu, India over a period of two years. The study was performed by using lean six sigma DMAIC tool.
Results
In the current study, implementation of Lean Six Sigma DMAIC methodology revealed significant decrease in guideline errors, irregular follow ups, improper antibiotic usage and prescribing errors. Correspondingly, Six Sigma level improved from 1.1, 2.47, 3.87, 3.35 to 1.57, 2.55, 4.02 and 3.61 respectively.
Conclusion
The study concluded that, by reducing antibiotic associated errors, such as inappropriate usage of antibiotics, prophylaxis use of higher end antibiotics, unrestricted duration of use and economic burden related to antibiotic treatment can be reduced. This can have a direct impact on improving patient safety and better clinical outcome.

An array of clinical manifestations, majority of which are relevant to dose and fade away after drug discontinuation, may accompany drug-induced nail abnormalities, but rarely do they endure over a long time. However, only a few groups of medications are reliably implicated in nail symptoms. Chemotherapeutic drugs have well-known effects on organs that include hair, skin and the digestive tract, which present clinically as exfoliative contact dermatitis, receding hair loss respectively. As a “skin” appendage, Nails are not an exemption. Patients undergoing systemic chemotherapy may experience an assortment of nail anomalies with chemotherapeutic drugs being the most common contributors. These alterations might only affect just one or many nails and could lead to discomfort and pain Nails. Transverse Lines can be passed down genetically or triggered by a range of illnesses and drugs. We report a case of a cancer patient who experienced transverse leukonychia as a result of antineoplastic therapy.

Alopecia Areata (AA) is an autoimmune condition characterized by scattered patches of hair loss on the body and scalp. Hair loss can be a cause of psychological stress and sufferers may suffer from social phobia, anxiety and depression. Even though there are many treatment options available in modern medicine, they have their own limitation which needs to be addressed. In Siddha system of medicine, a topical applicant named “Pancharatna Kalimbu” is used for the management of Alopecia areata, known as “Puzhuvettu” This medicine can be used a standalone drug in the management of Alopecia areata. As this is topical medicine, it can be administered to children who resist taking any kind of internal medicines, injections, or other treatments. Hence, this case report proves it efficacy which may be effective as a best alternate for treating children.

This case report outlines the clinical presentation and management of a 35-year-old female diagnosed with Darier disease, a rare autosomal dominant disorder resulting from an ATP2A2 gene mutation. The patient's atypical disease course, featuring facial involvement and a history of psychosis and depression with characteristic features, such as hyperkeratotic papules and nail changes, were noted was managed with a three-month isotretinoin regimen and concurrent antipsychotic therapy for coexisting depression and psychosis. This case highlights the need for a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to address both dermatological and psychiatric aspects in the management of Darier disease. The coexistence of psychiatric conditions in the form of depression and psychosis adds complexity to the clinical picture. This case emphasizes the importance of considering these factors in the diagnosis and treatment of Darier disease.

