
The study outlines the review of ocular films and polymers so far used by quick reference for the researchers. There is extensive research going on in the name of finding an accurate polymer that helps delay the release of drugs in ocular drug forms. The ocular film is a good idea if implemented properly, but finding a suitable polymer is a gargantuan task that has yet to be accomplished. Till now, researchers have extensively studied and compiled in the interest of reviewing all the available ocular films. To research and compile previous works on ocular films. Various sources of information collected were from the internet and research journals, which have been employed. Thanks to the extensive article collection of the team, it was possible to study and review all the available ocular films in the research. The article summarizes the ocular films' general preparation methods and evaluation tests. Ophthalmic preparation methods and eye diseases were discussed. The combination of drugs with polymers was discussed. This will help in a quick review of drugs and polymers that were successfully tried in making ocular films and the common evaluation approaches.

Global public health is threatened by the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. There is an increased risk of illness, complication, increased hospital stays and death as well as an increase in the amount of money spent on medical treatment. This has a significant impact on the clinical aspects of infections with the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria. The main aim of this review is to highlight the use of antibiogram in hospital and impact of antimicrobial stewardship program in fighting antimicrobial resistance. In addition, the study also focuses on the need of antibiogram and its development by creating the roadmap for antimicrobial susceptibility testing systems. The study also highlights policy documents on antimicrobial stewardship practices in India as well as at global level. In addition to this, the also highlights the process of antibiogram development and the need for an antibiogram in the current situation. Lastly, the study points out the role of hospital antibiogram in reducing antibiotic resistance.

The problem of infertility affects approximately 15 percent of couples in their reproductive years. Even after frequent, unprotected sexual activities for a year, or more, they are not able to conceive. Male infertility is a factor in more than a third of these couples. The cause of male infertility is low sperm production, abnormal sperm function, or blockages preventing sperm from being delivered. Infertility in men can be caused by illnesses, injuries, chronic health problems, lifestyle choices, and other factors. When you can’t conceive a child, it can be stressful, and frustrating, but there are several treatments available for male infertility. Sometimes signs and symptoms can be attributed to underlying problems. This includes an inherited disorder, hormonal imbalance, dilated veins around the testes, or a condition that prevents the passage of sperm. Male infertility is predominantly caused by varicocele, infection, abnormal ejaculation, antibodies that attack sperm, tumours, undescended testicles, hormonal imbalance, defects in the tubes that carry sperm, chromosome abnormalities, sexual dysfunction, and celiac disease. The oxidative biochemistry in sperm are addressed in this study.
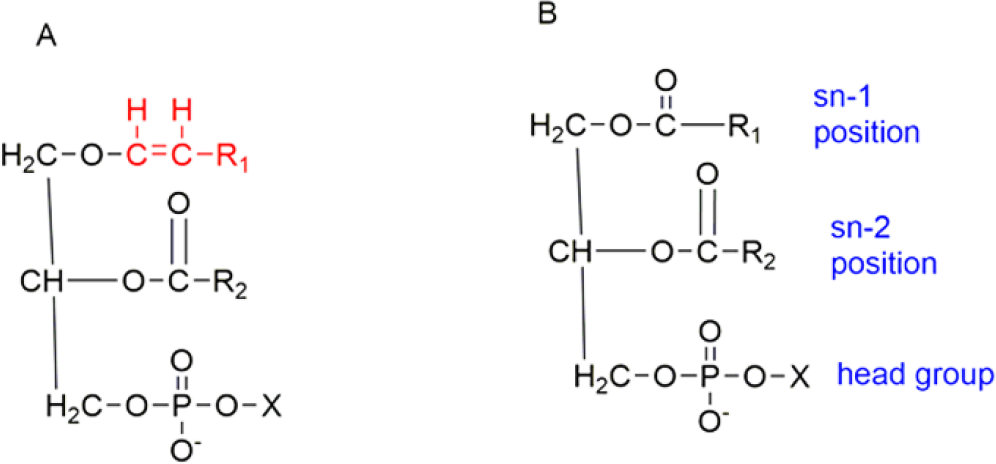
Plasmalogens, glycerophospholipids, can alleviate Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. It helps in neural communication, such as vesicular or membrane fusion and ion transport. It counteracts oxidative stress by acting on Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Plasmalogens may improve memory in Alzheimer’s patients as observed using Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-Cog). Plasmalogens are usually isolated from Ascidians and Scallops. In the current review, we discuss the role of plasmalogen in neurodegenerative disorders.

Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most common type of dementia, is a progressive neuro-degenerative disease severely affecting memory and cognitive function. It causes linguistic and visuo-spatial deficiencies, and behavioral problems like indifference, aggressiveness and depression as disease progresses advanced stages. No cure is available for Alzheimer’s, though symptomatic treatment improves memory and other symptoms. Natural products ease the symptoms of many kinds of diseases and offer a treatment option for many diseases at least successfully slowing the progress. Medicinal plants and plant products have been historically employed to improve brain function and treat memory disorders like amnesia, dementia. Though, various studies have described the utility of plants for treatment of Alzheimer’s, but with limited scientific evidence. Though, it has been reported that early start of utilization memory enhancing agents and brain tonics can be beneficial in AD. The present review is to summaries the herbal medicines which have reported to have some kind of CNS activity and may be utilized for slowing progression, symptomatic treatment and research in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and its related symptoms.
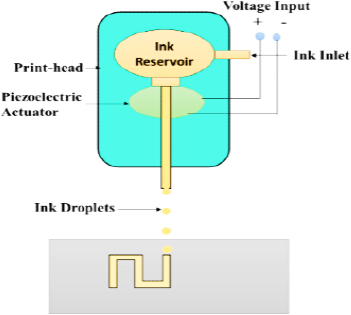
3–dimensional (3D) printing offers the chance to fabricate medications with more than a single active ingredient categorised by various properties and with diverse dissolution profiles. As a result, making composite medications may affect the decline in the number of used products. 3D printing in pharmaceuticals is a portion of the novel development called additive manufacturing, which means manufacturing three-dimensional compact substances from a digital file. Additive manufacturing is taken into consideration in the medical sector as it has the potential to advance treatment for certain conditions. The technology used mostly in the 3D printing of healthcare devices is termed powder bed fusion. Powder bed fusion is typically used for healthcare devices, as it can work with a wide variety of materials, including titanium, and nylon. Recent developments in technology and improved research in this sector can guarantee extra safe and effective cures. This technology appears to be an innovative tool that provides greater flexibility in medicine manufacturing and is likely to transform medication distribution schemes to a more diverse level in the future.

Complex medical data can be extracted using artificial intelligence, a branch of computer science. Their capacity to identify meaningful relationships within a data set can be applied in a variety of therapeutic settings for outcome prediction, diagnosis, and treatment. Artificial intelligence in medicine is developing swiftly. Artificial intelligence-powered medical technology is fast becoming practical clinical practice-related solutions. The increasing amounts of data generated by mobile monitoring sensors found in wearables, smartphones, and other medical equipment can be handled by machine learning algorithms. The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in many medical professions is discussed in this illustrative article from the perspectives of seven distinct fields: machine learning, intelligent robotics, image recognition technology, expert systems, artificial neural networks, and evolutionary computation. Additionally, it covers AI's prospective and current applications in medicine.

