
Qualitative research is a method of collecting data that does not involve numbers. It is used to understand human behavior, attitudes, beliefs and personality traits. It is different from quantitative research as it does not rely on numbers and statistics. Qualitative research questions encourage open-ended, non-biased and evolving responses. The study design is flexible and iterative, which can be adapted and refined throughout the research process. Purposeful sampling is a frequent method for selecting those who are the most pertinent to the study subject. Theoretically, saturation determines the number of observations when no discoveries or perspectives are forthcoming. Data can be collected employing many approaches, including Observation Methods, In-Depth/one-on-one Interviews and Document Review. The data is collected via audio recordings and tagged for analysis using qualitative information management software. Navigation, checklists, reflexivity and stakeholder involvement are all possible criteria for warranting research quality. Qualitative research serves different purposes, such as describing the existing situation, exploring the reasons or connections between things, evaluating the effectiveness of what exists and helping to develop new strategies. However, it has some limitations. Qualitative research is a valuable tool that can offer detailed insights and encourage openness. However, it can be time-consuming to deal with complex and evolving questions. Additionally, it may not be readily generalizable due to its limited number of participants and making systematic comparisons can be challenging as responses may vary subjectively. Despite these limitations, qualitative research can accurately simulate individual experiences and help avoid pre-judgments. This brief overview aims to provide an understanding of the different types, uses and evaluations of qualitative research methods, specifically in healthcare research.

Treponema pallidum (T. pallidum) transmits syphilis through sexual contact or perinatal transmission. T pallidum is widely known for being invasive and immune-evasive; its clinical symptoms are commonly mistaken for those of other diseases due to localized inflammatory responses to multiplying spirochetes. Complement fixation and precipitation/flocculation assays were developed in the early 20th century, and they were frequently combined to boost sensitivity and specificity because many cases were challenging. Despite a lifetime of negative anti-lipoidal serology, syphilis sequelae often develop. Treponemal tests (TPI, introduced in 1949) substantially improved sensitivity and reduced the number of false positives, but they were insensitive for primary syphilis. The teaching hospitals in Vienna have long confirmed that the TPHA discovers almost twice as many instances that aren’t found as the VDRL. Numerous active cases without VDRL reactions were discovered using the avidity/affinity index (Boltzmann Institute for Serodiagnosis, Vienna) as a substitute for the IgM antibody. Despite these improvements, Ontario’s Public Health Laboratory has discovered that gay men who are HIV antibody (+) selectively lose their treponemal antibody, making it hard to detect the incidence of syphilis.

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition causing joint inflammation and damage. Despite treatment progress, effective topical therapies pose challenges. Animal models, like Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) and Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis (AIA), mimic RA pathogenesis, aiding preclinical evaluation of topical treatments. By studying these models, experts can assess the efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of novel topical treatments, thereby accelerating their translation into clinical practice. Optimizing drug delivery, bioavailability and minimizing side effects are critical in formulation development. Animal studies refine parameters such as vehicle selection, drug concentration and application frequency for maximal therapeutic benefit. These models also deepen understanding of RA mechanisms, informing targeted topical therapy design against specific inflammatory mediators or immune cells. Lastly, animal models accelerate topical RA treatment development, providing vital data and mechanistic insights. Leveraging these models enhances formulation safety and efficacy, potentially improving patient outcomes.
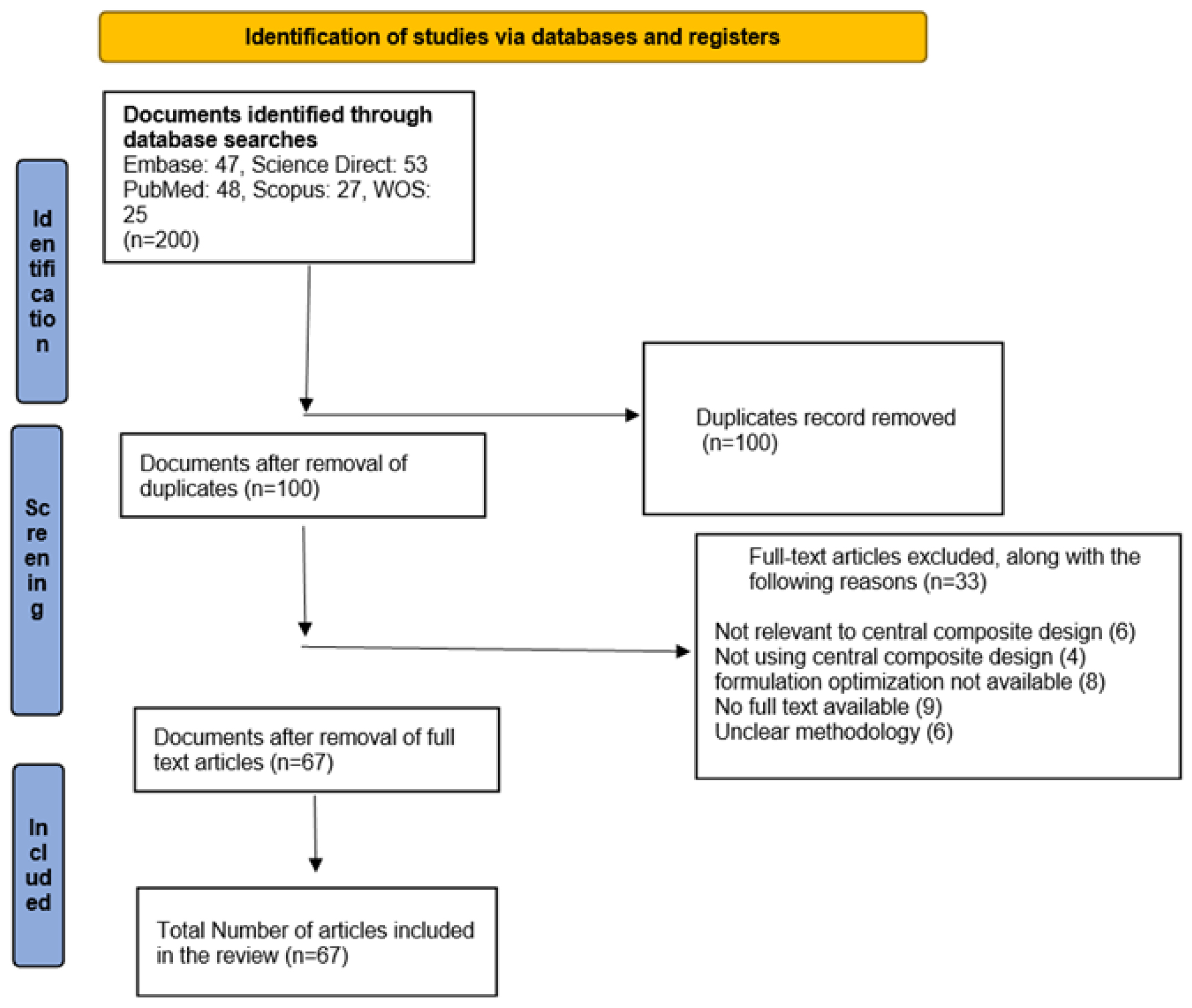
Design and optimization are pivotal in a pharmaceutical company’s formulation and manufacturing process. Various approaches and methodologies are employed in formulation design. A quantitative adjustment to a component, ingredient, or process variable is made while maintaining control over other independent components to monitor their influence on quality attributes. However, investigating these components together poses challenges, potentially leading to misinterpretation of experimental results. To resolve this, simultaneous design and development process modification can be achieved using the design of experiment methodologies, such as Central Composite Design (CCD). CCD effectively evaluates the interaction effects of numerous elements on product quality and outcomes. It has been successfully applied across various studies to develop and enhance formulations. This review provides insights into CCD, including its varieties, a comparison with other experimental designs, applications in pharmaceutical formulation, experimental design data analysis, optimization techniques, benefits and advantages, case studies, integration with Quality by Design (QbD) and regulatory considerations.
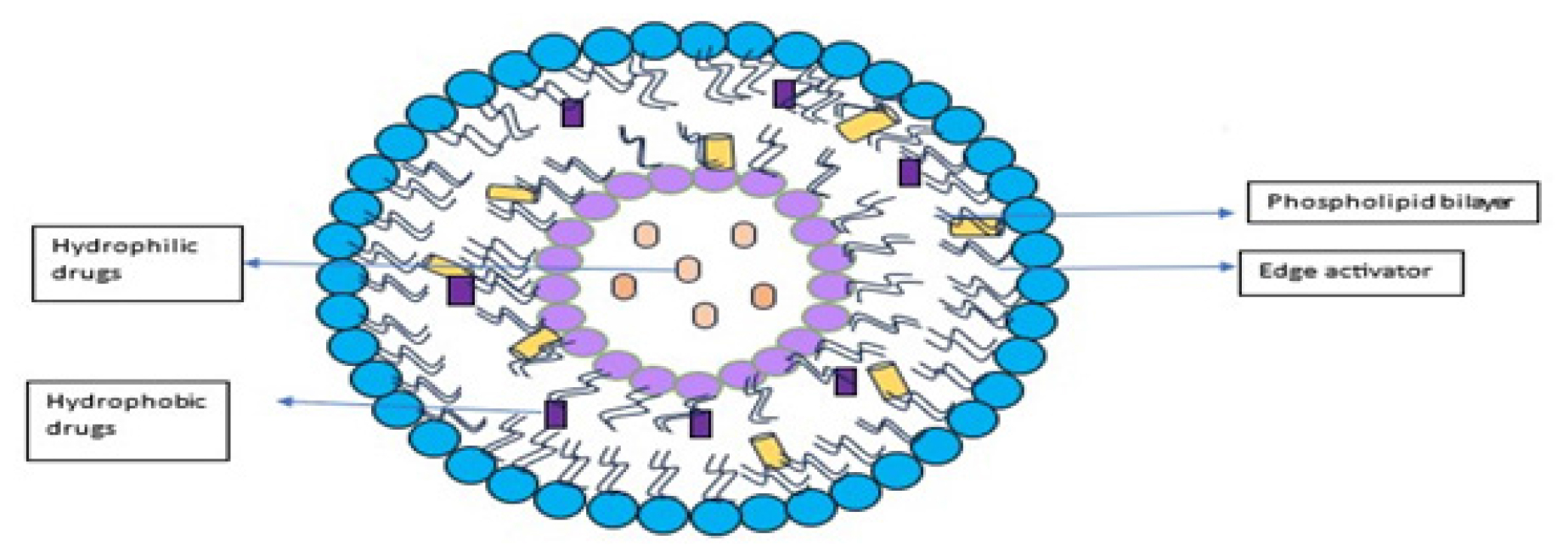
A potential development in medication administration, transferosomes are lipid-based vesicles that have been designed with edge activators, especially for transdermal and transmucosal uses. Transferosomes, which are mostly made of phospholipids enhanced with surfactants, are remarkably flexible and facilitate the effective passage of both hydrophilic and lipophilic medicines across biological barriers. Because of their deformability, drugs can more easily pass through microscopic pores and intercellular gaps. A wide variety of pharmaceuticals may be encapsulated in transferosomes, which have benefits include prolonged release patterns, defence against enzymatic degradation, and the ability to encapsulate both lipophilic and hydrophilic compounds at the same time. They are useful for systemic and topical drug administration due to their capacity to evade hepatic first-pass metabolism; they may also find use in targeted treatment and extended-release formulations. Despite their benefits, transferosomes have drawbacks, such as the high expense of Chemical instability and natural phospholipids. Exact control over vesicle properties is possible by a variety of production techniques, including as centrifugation, sonication, and thin film hydration. size analysis, entrapment efficiency, deformability, and stability assessment are all included in characterization approaches. Transferosomes are useful for delivering tiny molecules, proteins, and peptides. They can also be used to improve oral bioavailability, improve topical medication administration, and perhaps transform vaccine delivery and ocular applications.
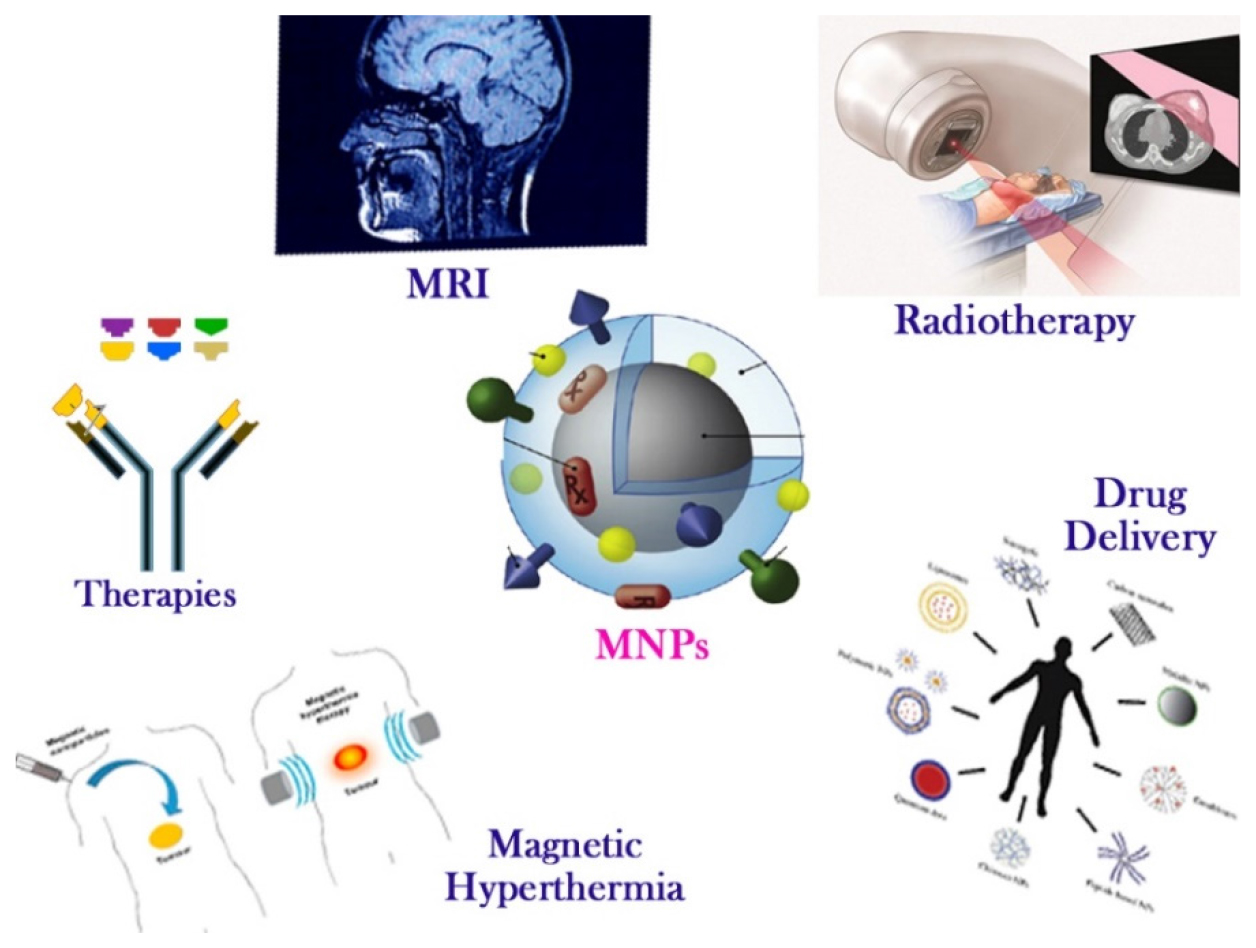
Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) are now being utilized more frequently in experimental research on cancer treatments, which has become one of the most difficult problems in medical science. The fundamental objective of this research is to use nanotechnology to effectively treat and eradicate advanced or metastatic cancer with the fewest possible negative effects. The fact that MNPs can be bound to chemotherapeutic medications, nucleic acids, synthesized antibodies, or radionuclide compounds is taken into account by drug delivery methods. Under the influence of an external magnetic field, MNPs can be guided and various treatment modalities can be used. This research examines the function of MNPs in cancer imaging and diagnostics as well as several MNP manufacturing techniques. In addition to all of these, information on the use of MNPs for the treatment of breast malignancies from clinical trials and scholarly prospection has been compiled.

Vitamin D has a crucial role in maintaining thyroid and immune function. In hypothyroidism, the gland is underactive and Vitamin D impacts this condition. Vitamin D regulates gene expression in thyroid hormone synthesis and influences the immune system, affecting overall thyroid health. From the literatures, it is evident that hypothyroidism is correlated with hypovitaminosis D. The immune-mediated properties of Vitamin D reduce the symptoms of hypothyroidism caused by autoimmune conditions. Understanding the correlation of Vitamin D with hypothyroidism is crucial as it holds potential therapeutic implications. Maintaining adequate Vitamin D improves gland function and prevents disease-related complications.

The gut microbiome is being frequently acknowledged for its impact on intestinal and extra-intestinal conditions, notably cancer. Here, diet is the most extensively researched modulator of gut microbiota among various environmental factors, demonstrating the ability to enrich its diversity and composition. Recent insights from clinical and preclinical trials emphasize the reciprocal influence between gut microbiota and anticancer therapies, impacting treatment responses and mitigating associated toxicities. Understanding these intricate connections is pivotal, given the potential of the gut microbiota to enhance the efficacy of existing chemotherapeutic agents while reducing their adverse effects. A systematic literature review was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar, employing keywords like “gut microbiome,” “cancer therapy,” “chemotherapy,” “diet,” and “microbial fermentation.” Thus, this review seeks to examine the interplay between the gut microbiome and cancer therapies, while also delving into nutritional strategies that can modulate the gut microbiome to improve cancer treatments.

Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD) have claimed millions of lives, despite the efforts of medical professionals. There are several treatment methods for blocking a few neurohormonal cascades; however, it is debatable because there are few hypotheses, which claim that in Heart Failure (HF), these systems tend to activate potential counter-regulatory mechanisms. Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitors (ARNI) are developed to modulate both Renin-Angiotensi n-Aldosterone-System and Natriuretic Peptide, regulating neurohormonal cascade in HF. LCZ696 (Sacubitril/Valsartan) is the first-in-class ARNI, approved for managing HF. Initially, ARNI was developed to manage Hypertension, later the FDA regulatory label was expanded for the management of HF. Dapagliflozin belongs to the class of SGLT2 inhibitors that have shown potentially beneficial effects in HF. Would the two medications, which have distinct mechanisms of action but a similar effect-a decrease in the risk of HF-show additive or synergistic effects when taken together? India, known as “The Chronic Heart Disease Capital of the World”, is accounting sharp rise in sudden cardiac death with young adults being the worst sufferers. This review inference that, using ARNI and Dapagliflozin together may have a larger positive effect on HF patients’ quality of life by lowering their need for hospitalization due to HF deterioration.

Drug interactions represent a significant challenge in modern medicine, as the concomitant use of multiple medications is prevalent in-patient care. Understanding the mechanisms behind drug interactions, accurately assessing their occurrence and adopting effective management strategies are critical to optimizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing adverse events. This research paper provides a comprehensive review of drug interactions, focusing on their underlying mechanisms, methods for assessment and the implementation of management strategies in clinical practice.

The global impact of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARSCOV2) is profound, with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) presenting a clinical spectrum that leads to multi-systemic failure, particularly affecting the pancreas and resulting in diabetes and cardiovascular co-morbidities. Diabetes, the more life-threatening manifestation of COVID-19, is associated with a 30% higher fatality rate. This review aims to explore the intricate relationship between Hyperglycaemia and hyper inflammation in individuals with post-COVID diabetes, emphasizing the risks of recurring hyperglycaemia and distinguishing it from conventional diabetes. Methodologically, data synthesis and extraction were conducted based on diabetes mellitus and recent studies on the impact of coronavirus, especially SARS, on the pancreas, utilizing articles from the Pubmed search engine. Hospitalized COVID-19 patients show a higher likelihood of concurrent conditions, including diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases. Factors contributing to post-COVID diabetes include age, co-morbidities, pre-diabetic status, pre-existing micro-angiopathic disease burden, stress and direct links to elevated blood levels induced by cytokine storms or hyperinflammation from the diabetogenic virus. In conclusion, this study highlights the potential disruptions in glucose production and metabolism following COVID-19 infection. The recommendation is for individuals who have experienced COVID-19 to undergo rigorous glycemic screening approximately a month post-infection. The findings underscore the importance of monitoring and addressing alterations in glucose homeostasis as part of post-COVID-19 care. Further research and clinical observation are essential to enhance our understanding of the intricate relationship between COVID-19 and glycemic control. The key message emphasizes the comprehensive review of the interplay between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the heightened risk of diabetes, advocating for vigilant post-infection glycemic screening and revealing potential disruptions in glucose metabolism.

Background
Medicated oils and Clarified butter are often utilized in the Traditional System of Indian Medicine for internal and external use. To improve the durability and efficacy of therapeutic oil unique processing is advocated known as Murchhana. Specific ingredients are mentioned for each oil. The current work seeks to conduct a comparative analytical evaluation of processed and unprocessed castor oil.
Materials and Methods
Both the oils were analyzed for rancidity, specific gravity at 25°C, refractive index, iodine value, saponification value, acid value, peroxide value, free fatty acids, and HPTLC.
Results
There was a significant difference between unprocessed and processed castor oil. Physicochemical and HPTLC analysis revealed significant differences in all samples, indicating that extra active chemicals were obtained in the processed oil. Saponification Value was increased in processed oil, however, iodine value, and acid value were found to decrease indicating the enhancement of the shelf life. Thus, utilizing adopting processing techniques the shelf life of the oil can be improved.
Conclusion
Based on the results of analytical criteria, it implies the significance of processing the castor oil as mentioned in the Ayurvedic texts.

Background
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is most prevalent global health problem, develops due to accumulation lipids in the hepatocytes in the form of Triglycerides (TG) and Free Fatty Acids (FFA). Traditional healers recommend seeds of Cucumis melo Linn as a liver tonic as well as for its treatment of liver cirrhosis, however its hepatoprotective mechanism have not been explored.
Objectives
To investigate significant molecular mechanism of C. melo against liver cirrhosis via in vivo analysis followed by in silico.
Materials and Methods
HFD was used for the induction of hepatotoxicity in mice and Silymarin as a standard control. The physical parameters were measured throughout the study along with antioxidant, serum biomarkers and histology of liver. Further, System biology tools were used to predict the possible mechanism of action. Docking studies were carried out with modulated phytocompounds against FXR protein target.
Results
C. melo. Extract and fraction ameliorated the HFD induced oxidative stress and histological changes. Additionally, improved liver biochemical parameters such as AST, ALT, ALP, serum bilirubin, total bilirubin, LDL, VLDL, TC and, TP were seen remarkable significant effects. Furthermore, System biology revealed the 16 phytocompounds of C. melo Linn. potentially regulate the PPAR signaling. Among them, Euphol phytocompound was predicted to interact with secreted FXR and may contribute to reduced hepatotoxicity.
Conclusion
The results suggests C. melo as a promising therapeutic agent for hepatotoxicity by reducing the symptoms and stress associated with diseases condition which may be due to the regulation of multiple protein via multiple phytocompounds.

Objectives
Alzheimer’s disease is primarily caused by neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta Aβ(25 35) peptide accumulation and increased levels of Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme (AChE). Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors report for the effective management of cognitive and motor disorders. In the current study the impact of Diplocyclospalmatus Methanolic (DPM) seed extract and its Chloroform (DPC) fractions were investigated in mice with Amyloid beta (Aβ)-induced experimental Alzheimer’s disease.
Materials and Methods
Acute toxicity study was performed based on the guidelines of OECD 423 and doses were selected. Mice were administered with standard Donepezil (5 mg/kg/oral) and two doses each of DPM and DPC daily for 21 days (200 mg/kg and 400 mg/kg/oral). Aβ was given by Intra Cerebro Ventricular (ICV) injection in a single dose 3 mg/kg. Cognitive abilities were assessed using the conditioned avoidance test, the rectangular maze and Y-maze. On 22nd day mice were sacrificed, then isolated brain homogenate used for estimation of biochemical parameters such as reduced Glutathione peroxidase (reduced GSH), Malondialdehyde (MDA), nitrite level and AChE levels.
Results
Administration of DPM and DPC extracts effectively reduces behavioral and biochemical abnormalities in dose dependent way.
Conclusion
Diplocyclospalmatus seeds showed neuroprotective effect on Aβ-induced AD in mice due to their antioxidant and AChE activity.

Background
The present study is designed to develop a novel dosage form i.e. microemulgel which will enhance the rate of absorption in the systemic circulation and ultimately enhance the pharmacological effect of the Mentha piperita L. extract as anti-inflammatory agent. Its primary components include with constituents including menthol (46.32%), menthofuran (13.18%), menthyl acetate (12.10%), menthone (7.42%) and 1,8-cineole (6.06%).
Materials and Methods
The research aimed to formulate and assess herbal microemulgel containing M. piperita extract, focusing on its in vitro anti-inflammatory properties. M. piperita herb extraction was carried out using a hydro-alcoholic solvent, followed by phytochemical analysis. Four separate sets of herbal microemulgel were crafted and underwent a series of assessments, encompassing pH levels, spreadability, viscosity, consistency, appearance, color and ease of washing. Additionally, the in vitro anti-inflammatory potential of both the extract and the microemulgel formulation was assessed using the HRBC membrane stabilization assay and the protein denaturation assay.
Results
The findings of this study suggest that the newly developed herbal microemulgel, enriched with M. Piperita extract, exhibits promising anti-inflammatory effects.
Conclusion
The M. piperita microemulgel exhibited a remarkable 94.35% drug content with high solubility and compatibility of the drug with the excipients. Permeability studies revealed that the M. piperita microemulgel achieved 94% permeability within 48 hr, showcasing enhanced drug permeability facilitated by the microemulsion-based gel system. Moreover, the formulated microemulgel demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory activity. It can be concluded that topical herbal M. piperita microemulgel has potential for future applications in this regard.

Background
Five-membered heterocycle with one neighbouring nitrogen atoms is present in the indole nucleus. Heterocyclic substances feature two adjacent benzene and pyrrole ring atoms. Indole are heterocyclic compounds with one oxygen ring that have a benzoannelated - pyrrole ring. Indole derivatives are highly valuable chemical synthesis and medicinal intermediates. Recent years have seen a surge in interest in the effective synthesis of indole blocks and associated functionalization’s, particularly the alkylation of indoles. The two following factors will be the main emphasis of this review: i) Recent advancements in the alkylation of indoles, namely those involving the N1-, C2- and C3-positions and the synthesis of indoles, which was facilitated by transition metals.
Materials and Methods
Benzoic acid and ethanoic acid, propionic acid, hydroxylamine, 2,5 Dichloro aniline are used for the synthesis of indole derivatives were used for the synthesis of indole.
Results
Compared to indomethacin, the anti-inflammatory results for the substances or their derivatives like N2-(biphenyl-2-yl)-4-chloro-N1-(5-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)-4-am inobenzene-1,2-diamine NA5 (Scheme 1B); N2-(biphenyl-2-yl)-4-chloro-N1-(5-chloro-1 H-ind ol-1-yl)-3-aminobenzene-1,2-diamine NA6 (Scheme 1B) and N2-(biphenyl-2-yl)-4-chloro-N1- (5-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)-2-aminobenzene-1,2-diamine NA7 (Scheme 1B).
Conclusion
Examined were the anti-inflammatory properties of the substances in the title and their derivatives. The compounds containing indole derivatives with an electron-withdrawing group have a higher activity than those containing an electron-donating group, according to research on the link between structure and activity. Summarising the data from the previously reviewed literature, we can say that indole has a broad spectrum of biological activity. Numerous opportunities exist to investigate indole for new therapeutic uses. Researchers worldwide will benefit from this study’s coverage of the chemistry of indole derivatives in the design and synthesis of new pharmaceuticals that might be utilised to treat a range of diseases.

Background
Pharmaceutical sponsors have a significant responsibility in gathering and overseeing the storage of leftover human biological samples. Understanding the proper utilization and potential risks associated with these stored specimens is crucial for pharmaceutical sponsors. Educating these sponsors on biological sample research is imperative. Hence, the present study aims to assess, evaluate the Knowledge, Attitude and Practice (KAP) among pharmaceutical sponsors in relation to the utilization of surplus human biological samples for future research.
Materials and Methods
A study was conducted in which pharmaceutical sponsors participated in both pre- and post-intervention assessments to evaluate prospective changes. Prior to the survey, self-prepared and validated Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices (KAP) questionnaires were distributed among the sponsors, uncovering certain gaps in their knowledge, attitudes and practices. Following this, health education was administered through oral sessions and leaflets. A follow-up survey was conducted one month later using the identical set of questionnaires to assess any changes in KAP among the pharmaceutical sponsors.
Results
A research recruited 52 participants from pharmaceutical sponsors, with men greater than women by 75 percent. Most of participants (69.2%) were between the ages of 20 and 30, with 73.1% having a pharmacy background. In addition, 82.7% had between 1-5 years of work experience. Senior Clinical Research Associates (CRAs) accounted for 30.8% of participation, while CRAs made for 23.1%. The research project begins with a pre-test to assess participants’ knowledge, attitude and practices, followed by an educational intervention and a post-survey one month later. The McNemar-Bowker test revealed significant improvements in scores (p-value<0.005) after the intervention.
Conclusion
Educating pharmaceutical sponsors about leftover bio specimens reduces misuse as well as helps in understanding the ethical issues involving leftover bio specimen studies.
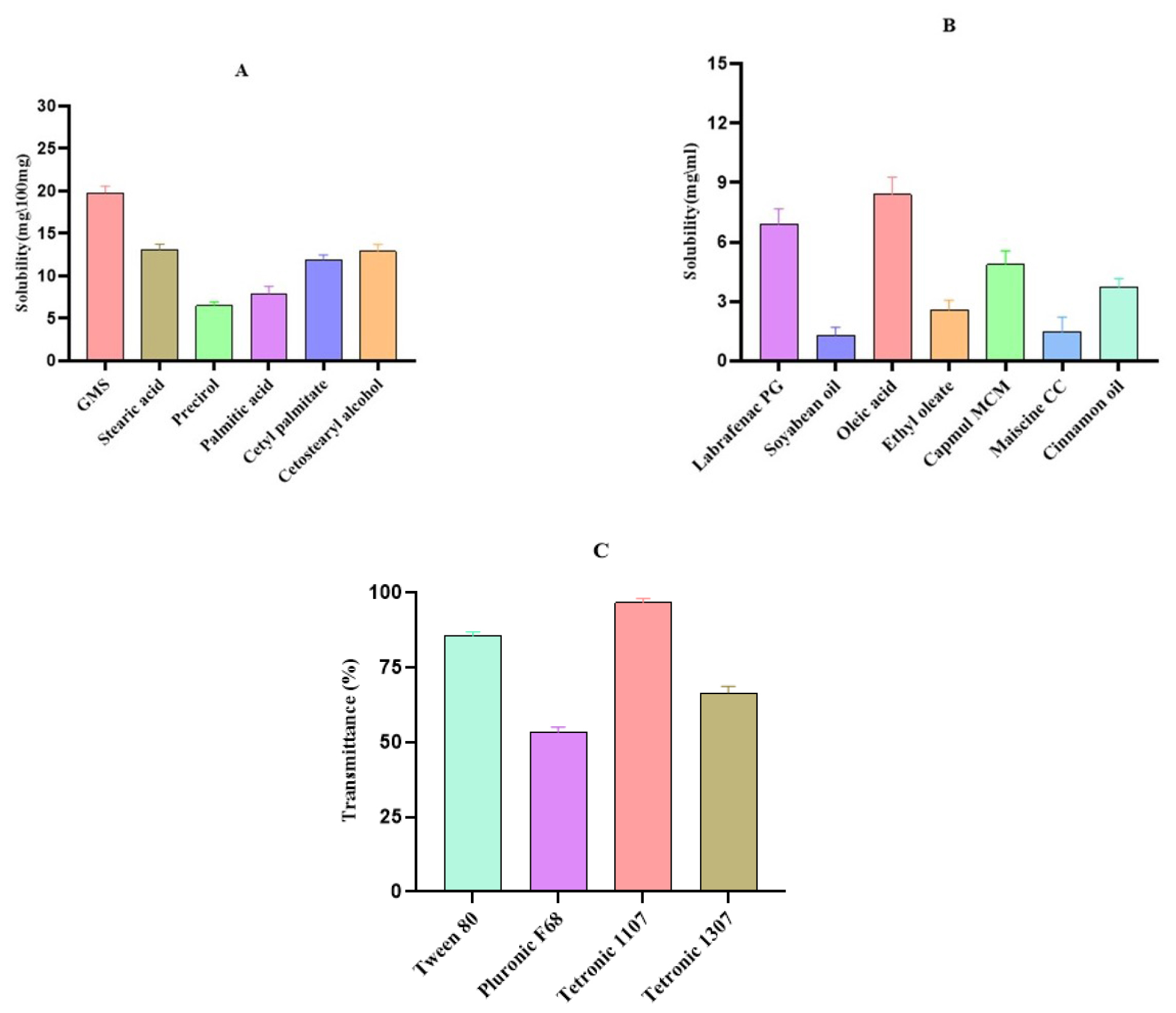
Background
Gemcitabine (GEM), a Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) class-III drug, holds promise for non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Utilizing lipid-based nanoparticles for targeted delivery has proven effective in cancer therapy. Biotin receptors, overexpressed in various solid tumors, offer a specific target for enhanced chemotherapy efficacy while minimizing side effects. Hence, this study aimed to formulate biotin-coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) with Gemcitabine can be delivered to specific tumors by electrostatic attraction.
Materials and Methods
Nanostructured Lipid Carrier loaded Gemcitabine was formulated using Oleic acid and Glyceryl monostearate as lipids, with Tetronic 1107 as the surfactant. Formulations were optimized using a 2-factor, 3-level full factorial design approach with Design Expert software. Size of particle, Zeta potential, Polydispersity index, Encapsulation efficiency, Scanning Electron Microscopy, phase contrast microscopy, drug release and in vitro cytotoxicity against A549 cells were assessed for characterization.
Results
The optimized Gemcitabine-loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier formulation exhibited a particle diameter of 194.5 nanometer (nm) and Biotin-Gemcitabine- Nanostructured Lipid Carrier showed a size of 203.1 nanometer. In vitro drug release efficiency of about 95.125% during 8 hr for Gemcitabine-Nanostructured Lipid Carrier and 96.04% during 24 hr for Biotin-Gemcitabine-Nanostructured Lipid Carrier, suggesting prolonged circulation for the latter. Cytotoxicity assays revealed significant reduction in cell viability and induction of cytotoxic activity Gemcitabine-loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-biotin at low concentrations in A549 cells.
Conclusion
The developed biotin coated Nanostructured Lipid Carrier present a promising strategy for targeted delivery of Gemcitabine to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). These nanocarriers could provide a targeted and efficient delivery platform to tumor cells. Further in vivo investigations are warranted to validate their safety and therapeutic effectiveness.

Background
In this study, neem oil’s therapeutic potential against bacterial inflammations is explored through nanoemulsion technology. Despite its historical significance in traditional medicine, neem oil formulations face challenges such as limited stability and poor solubility. Nanoemulsions offer a promising solution by enhancing neem oil’s efficacy, stability, and patient acceptability. Utilizing Response Surface Methodology (RSM), specifically Central Composite Design (CCD), enables systematic optimization of nanoemulsion formulations, enhancing their therapeutic potential.
Materials and Methods
In this research, the Central Composite Design was instrumental in fine-tuning parameters like the concentration of surfactant (A), speed of homogenization (B), and running time of homogenization (C). These variables were explored across three different levels. Particle size, serving as the dependent variable, was assessed as the response to variations in these independent factors. Mathematical equations and response surface plots were used to understand the relation between the factors influencing the outcome and the resulting dependent variable.
Results
The optimized CCD model has a particle size of 97.9 nm, a zeta potential of -21.0 mV, and a PDI value of 0.512. Carbopol 934 was utilized in formulating the nanoemulgel. The observed responses closely resembled the anticipated outcomes from the optimized process. Morphological analysis and in vitro release studies were employed to characterize the prepared nanoemulgel formulation.
Conclusion
The Response Surface Methodology facilitates the formulation of neem oil emulsion with the smallest droplet size possible. Furthermore, the nanoemulgel exhibited significant antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus).
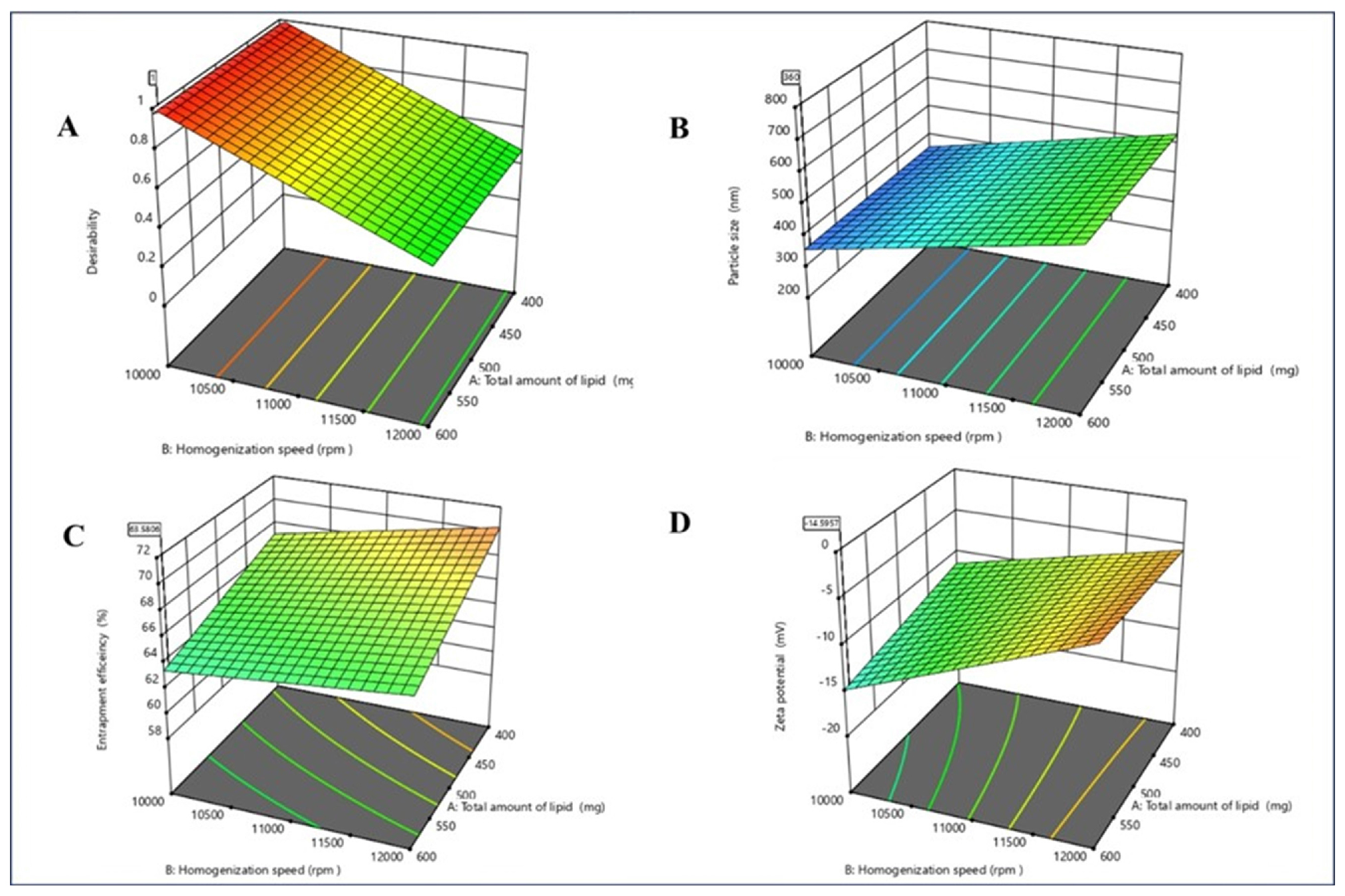
Background
Nano-structure Lipid Carriers (NLCs) are small spheres extending in scale from 10 to 1000 nanometres comprised of biocompatible and biodegradable lipids. These spheres can encapsulate both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, preserving them from degradation and increasing their distribution to the intended place in the body. Imipramine, a tricyclic antidepressant, has been investigated in hamster model at 5-10 mg/kg for experimental leishmaniasis. The goal of this research is to develop Imipramine in a nano-structured lipid carrier formulation for targeting macrophage cells.
Materials and Methods
Imipramine-loaded NLCs were created employing Glyceryl Monostearate (GMS) as the solid lipid constituent alongside oleic acid as the liquid lipid, while tween80 acted as the surfactant. The process of hot homogenization was employed to prepare the NLCs. The formulation was optimized using 23 factorial designs using design expert software. The optimised formulation was further used for the preparation of mannose functionalized imipramine-loaded NLCs.
Results
The IMP-NLC opt and M-NLC show a globule size of 348.5±0.81 nm and 459.4±0.28 nm with encapsulation efficiency of 61.6±0.326% and 64.48±0.408%, respectively. The drug release in vitro demonstrates a dual-phase pattern, featuring an early rapid sudden release followed by a gradual and slower release. The surface morphology, drug release kinetics and stability were also used to characterize the prepared NLCs.
Conclusion
This study concludes that nanostructured lipid carriers demonstrate considerable encapsulation efficiency, release and stability for further pre-clinical investigation.

Background
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) is frequently associated with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), often under diagnosed and inadequately treated. Hence, this study aimed to ascertain the prevalence of CKD-induced RLS, exploring associated factors, pharmacotherapy and its impact on patients’ quality of life.
Materials and Methods
An observational prospective study conducted at Dhiraj General Hospital, Vadodara, from November 2022 to March 2023 included 246 CKD patients. Screening for RLS symptoms led to further evaluation and treatment in the Neurology department. Patients were re-evaluated after one month to assess treatment outcomes.
Results
Analysis of 246 patients revealed a 6.91% prevalence of RLS in CKD. Factors contributing to RLS included anemia, advanced CKD stages and prolonged dialysis. Female gender emerged as a CKD risk factor. Pramipexole, Syndopa and Ropirinole effectively treated RLS in CKD patients.
Conclusion
RLS substantially diminishes the quality of life in end-stage renal disease patients. Identification and management of contributing factors hold promise for improving outcomes and quality of life in CKD patients with RLS.

Background
Diverse beliefs and perceptions on the use of COVID-19 vaccines and drugs have been affecting the acceptance of COVID-19 vaccination and maternal and child health. Further, inappropriate use of antibiotics induces development and spreads antimicrobial resistance.
Materials and Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate COVID-19 vaccination status and rational use of drugs in women during the recent pandemic.
Results
The use of medicines in pregnant (94.1%) and non-pregnant (96.0%) is highly prevalent. Prescription of two drugs (24.2%) and three drugs (23.7%) was seen in non-pregnant and pregnant women, respectively. Only 20.4% of pregnant and 43.7% of non-pregnant women received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine either Covishield or Covaxin. In addition, ‘Watch’ antibiotics were prescribed relatively more than ‘Access’ antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed ‘Access’antibiotics were doxycycline and clindamycin in pregnant and non-pregnant women, respectively, whereas azithromycin was the frequently prescribed ‘Watch’ antibiotic in both groups.
Conclusion
Polypharmacy was common, the acceptability of COVID-19 vaccination was less and the prescription of ‘Watch’ antibiotics was more in both pregnant and non-pregnant women. Importantly, there is scope for improvement in promoting vaccination, education on the WHO AWaRe antibiotics and rational prescribing of antibiotics in women of childbearing age.

Background
Drug-Related Problems (DRPs) are prevalent among patients with acute heart failure, potentially leading to adverse outcomes. Understanding the prevalence and nature of DRPs is crucial for improving patient care and outcomes.
Purpose
This prospective observational study aimed to assess the prevalence of DRPs among patients with acute heart failure admitted to the Intensive Critical Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital.
Materials and Methods
Data were collected from 150 patients using a standardised DRP Data Collection form. The Cipolle Classification was used to assess Drug-Related Problems. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 28.1.1, with Pearson Chi-Square employed for p-value calculation.
Results
Comorbidities were present in 96% of patients, with 56% prescribed between 11 and 20 drugs. Hospitalisations lasting 4 to 6 days were reported in 41.3% of cases. DRPs were identified in 92% of patients, totalling 344 instances. Adverse drug reactions and unnecessary drug therapy, particularly involving diuretics and antiplatelets, were the most common types of DRPs. Polypharmacy demonstrated a significant association with an increased risk of DRPs.
Conclusion
This study highlights the common occurrence of DRPs among hospitalised heart failure patients. The findings underscore the need for pharmacist interventions to mitigate DRPs and improve patient outcomes. By contributing to the optimisation of pharmaceutical care in this patient population, this study provides valuable insights for healthcare providers aiming to enhance the quality of care for patients with acute heart failure.

Background
Periodontitis is a common chronic inflammatory condition in adult population affecting both the hard and soft tissues surrounding the teeth. Bacteriotherapy is an alternative way to suppress infections by using probiotic bacteria which have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Till date many studies have been done to check the efficacy of probiotics delivered systemically and a very few as local drug delivery. Therefore, the present study was designed to clinically and microbiologically evaluate the efficacy of local drug delivery of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis 2*109 CFU/g gel as an adjunct to conventional mechanical periodontal therapy in comparison with tetracycline gel in stage II, III periodontitis patients.
Materials and Methods
45 systemically healthy Stage II, III periodontitis patients were selected and randomly allocated into 3 groups. All the groups received scaling and root planing, Group 2 and Group 3 received local drug delivery of probiotic and tetracycline gel respectively. Clinical and microbiological evaluations were done at baseline, 1 month and 3 months following the treatment in all the groups. Microbiological analysis was carried out by RT PCR.
Results
At 3 months evaluation, all the clinical and microbiological parameters showed significant improvement in all the groups. On inter group analysis statistically significant improvement was seen in Group 2 and Group 3 when compared to Group 1. Group 2 and Group 3 showed no statistically significant difference.
Conclusion
Local drug delivery of Bifidobacterium gel can be a useful adjuvant to scaling and root planing in periodontitis patients. Further long-term studies are required to evaluate the action of probiotics in periodontitis.

Background
Hypothyroidism is the most prevalent endocrine condition among women of reproductive age, affecting 3-5% of the entire pregnant population. If left untreated, it can lead to serious maternal and fetal complications. Knowledge, Attitude and Practice (KAP) surveys are quantitative approaches employed to assess these aspects within a predetermined population utilizing standardized questionnaires.
Materials and Methods
A prospective interventional study was conducted in the Obstetrics and Gynaecology department of a tertiary care hospital. Different educational modalities, namely Patient Information Leaflet (PIL) for Group A and Audio-Visual Aids along with PIL for Group B, were used through pharmacist intervention. Data were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 26.
Results
Group A showed moderately significant improvement in the practice domain (1.33±3.29; p<0.05), though no statistical significance was seen in the knowledge and attitude domains. In Group B, the overall pre-post data showed statistically significant improvement in all three domains, with mean improvement scores of 1.34±2.60, 0.77±1.88 and 3.71±2.78 in the knowledge, attitude and practice domains, respectively.
Conclusion
The study identified gaps in the knowledge and management of hypothyroidism among pregnant women, which increase the risks and complications during pregnancy. The audio-visual education modality was more effective in addressing these gaps compared to the written Patient Information Leaflet (PIL).

Ebstien anomaly is a rare heart problem present at birth and has a varied clinical course, it’s a congenital heart defect of the tricuspid valve. We hereby describe a 13-year-old child, was presented with history of Ebstien anomaly with Ostium secundum Atrial Septal Defect (OS ASD) was diagnosed at 1 year of age, but surgical correction was not done in early decade due to financial problem. At admission, child was in shock and saturation was not maintaining, Echocardiogram examination revealed Congenital Heart Disease (CHD), Ebstien anomaly, RA/ RV dilated, atrialised Right Ventricle (RV), Septal Tricuspid Leaflet (STL) displaced to the origin distance 5.6cm was noted, Grade 2+ Tricuspid Regurgitation (TR), Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure (PASP)-28 mmHg, no Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), normal Biventricular function. Child needed immediate surgical correction. Child was discharged with referral letter to higher centre.

This case report presents the clinical scenario of a 22 years old female patient with decade long history of seizure disorder and is on chronic anti-seizure management therapy. The patient’s initial symptoms manifested as lesions over the oral cavity, over the period of time the lesions progressed to scalp, chest and buttocks. Pemphigus is a rare heterogeneous group of autoimmune disease that affects the skin and the mucous membrane. A combination of inappropriate activation of host B lymphocytes producing intracellular ImmunoglobulinG antibodies and biochemical interactions results in the drug-induced pemphigus. Acantholypsia is the term for the process by which these auto antibodies target the desmogleins and split the cells in the epidermis. This case emphasizes the requisite for further research on understanding the effect of anti-seizure therapy.

Diabetes mellitus-related lower extremity amputation increases health burden and reduces patients’ quality of life, mortality and morbidity rate in a country like India. The most common complication in DM patients is uncontrolled hyperglycemia and foot ulceration. We report an unpredicted occurrence of right leg amputation in diabetic amputee patients. A 46-year-old male patient developed a complication to his contralateral limb due to poor negligence even after his first above-knee amputation; the patient was again readmitted for the below-knee amputation and hyperglycaemia. Although all the major complications of DM like hyperglycemia, cataracts, diabetic foot and diabetic foot amputation were found in the same index patient. The risk of amputation is high in diabetic patients and the prevalence of amputation is even extremely high in diabetic smokers. Hence proper lifestyle modification is needed along with dietary approaches to prevent and manage diabetes related complications. Regular foot examination and patient education are necessary which alerts the patient and family members to avoid the major risk of DM complications.

This case report presents the surgical management of a fibroadenoma in the left breast of a Nineteen-year-old female. The patient was exposed with the complaint of a palpable lump in her left breast, prompting further investigations. Ultrasonography revealed the presence of a lesion consistent with fibroadenoma. Subsequently, the patient underwent surgical excision of the lesion to alleviate discomfort and address diagnostic concerns. The procedure involved a Circumareolar incision followed by meticulous dissection and excision of the fibroadenoma lump. Postoperative evaluation confirmed successful removal of the lesion with resolution of associated symptoms. This case uplifts the importance of prompt diagnosis and appropriate management of benign breast masses in young patients to alleviate anxiety and ensure optimal positive outcomes.

