
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a sexually transmitted disease that can be passed from partner to partner, mother to child, or through blood exchange using infected syringes. AIDS symptoms might vary depending on characteristics such as age, gender, and physical activity. Headaches, muscle and joint discomfort, rashes, diarrhoea, weight loss, coughing, night sweats, sore throat, stomatitis, swollen lymph nodes, malaise, oral yeast infections, shingles (herpes zoster), and lung infections are all common symptoms. The Food and medication Administration (FDA) of the United States authorised Lenacapavir, a novel AIDS therapy medication, in 2022. Lenacapavir is a capsid inhibitor available in tablet and injection form that directly targets the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) Capsid Protein. Various research and papers, like the Capella study, which assessed the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous Lenacapavir, were used to assess the safety and efficacy of Lenacapavir. The Calibrate study shed light on the absence of phenotypic resistance to Lenacapavir in HIV Gag cleavage site mutants and isolates resistant to existing medication classes. These studies also included data from a proof-of-concept clinical research on HIV patients examining phenotypic resistance to Lenacapavir and its efficacy as a monotherapy. The approval of Lenacapavir represents a viable new therapy option for those living with HIV. Its method of action, as well as promising safety and efficacy results from numerous studies, offer hope for better outcomes in the treatment of this severe disease.
Background
Terminalia arjuna is an evergreen tree commonly referred as Arjuna, widely distributed in India and is a prominent member of the genus Terminalia. It has been discovered that the various plant parts, including the root, leaf, bark, fruits, and seeds have unique medicinal property. Among them, bark part is found to have and plethora of bioactive compounds and rich in medicinal property, especially for its cardiovascular properties.
Materials and Methods
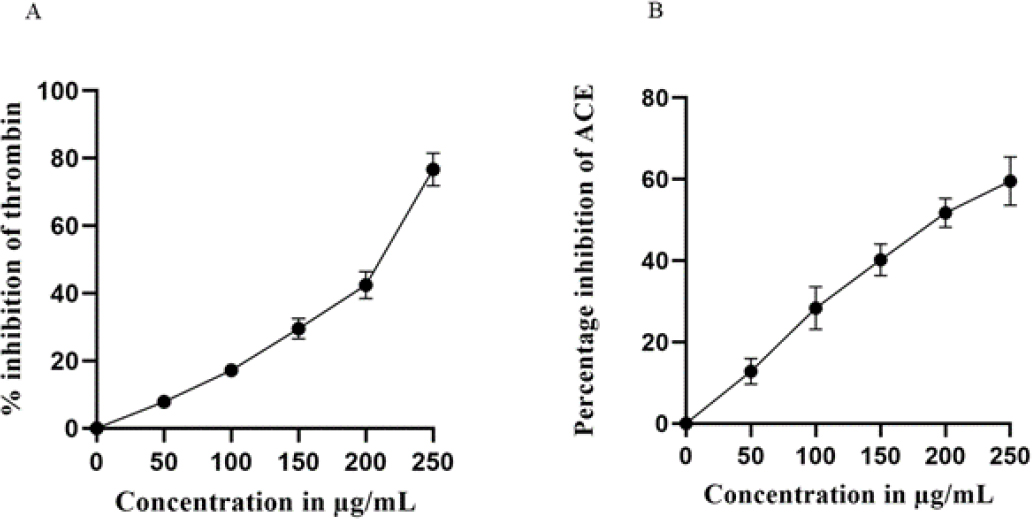
In the current investigation we have developed a standardized extract of T arjuna bark called Cardiboost, which contains 1% arjunolic acid. Cardiboost was used to examine in vitro thrombin and ACE enzyme inhibition. Additionally, MTT assay was used to measure cell viability of H9c2 cardiomyocytes, western blot experiments were performed to measure the levels of antioxidative enzyme levels CAT and SOD and the expressions of cell apoptosis regulatory proteins PARP1, Casp antiapoptotic properties to elucidate Cardiboost ability to prevent H9c2 cardiomyocytes cells suffering from oxidative damage induced by H2O2.
Results
Cardiboost, exhibited potent thrombin and ACE inhibition property, with IC50 values of 111.88μg/mL and 196.66 μg/mL respectively, Furthermore, Cardiboost, averted the cell death and significantly increased the levels of antioxidant enzymes CAT and SOD which was subsided in presence of H2O2, and Cardiboost protected the mitochondrial events and reduced the apoptotic effects in H2O2-induced oxidative stress.
Conclusion
Cardiboost could shield H9c2 cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress and may also be used as a medicinal product to prevent oxidative stress in cardiac damage.

Background
Tridaxprocumbens is an herbal plant that has been used for many centuries. It has shown promise in treating various medical ailments, including skin infections, burns, and wounds. The plant has several active ingredients, such as triterpenes, ursolic acid, quercetin, and tridaxin, all of which have potent anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant, and wound-healing qualities.
Materials and Methods
Lipid-based nanocarriers called ethosomes have drawn much interest in studying six formulations with varying amounts of ethanol and lecithin created in the study. Numerous criteria, including globule size, shape, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency, and in vitro drug release, were evaluated in detail for the ethosomal formulations.
Results
The study’s findings showed that every formulation had spherical and unilamellar characteristics, with entrapment efficiencies ranging from 57 % to 75 %, globule sizes between 122.6 to 910.3 nm, and zeta potentials between -25.06 to -52 mV. The invitro release tests demonstrated the medication’s consistent, long-term release from ethosomal vesicles.
Conclusion
The results of further evaluation studies indicate that the F5 ethosomal formulation, which contains quercetin as an active ingredient, had the highest levels of entrapment efficiency. The release kinetics were consistent with a Fickian zero-order drug release and diffusion pattern, showing both penetration and prolonged drug action.
Background
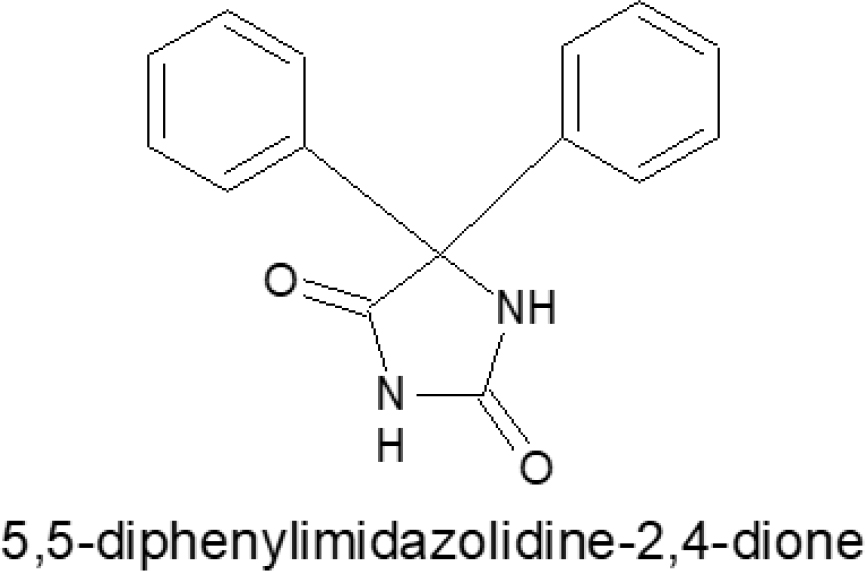
A heterocyclic hydrocarbon having a 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine heterocyclic ring that possesses distinctive fundamental structural characteristics. It is a fused ring of aromatic di-benzene and imidazolidine. The flexible heterocyclic molecules in 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine that have two nitrogen atoms. The biological activity of the 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine ring and its derivatives is significant and encouraging. We produce a variety of 4-(chloroethoxy)-3- [2,4-dioxo-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-1-yl) carbonyl] benzene sulfonic acid and its derivatives in this investigation. In literature survey and molecular docking; it was confirmed that 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione gives anticonvulsant effects. The pharmacological samples were examined for their ability to prevent convulsions using the strychnine-induced convulsion method.
Materials and Methods
Benzoin; Benzil; Urea; Glacial Acetic Acid; 4- Amino Benzoic Acid; Con. HNO3; Formic Acid; 2- Nitro Aniline; 4- Nitro Aniline; Aniline; Acetyl Chloride; Formic Acid; 4- amino Phenol are used for the synthesis.IR, NMR and MS are used for interpretation.
Results
Our research led us to the conclusion that a variety of compounds have strong anticonvulsant properties. The compound 4-(2-chloro-N-(2-phenoxyethyl) aniline)-3-[2,4-dioxo-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-1-yl) carbonyl] sulfonic acid (SPD5)- (scheme II A); 4-(3-chloro-N-(2-phenoxyethyl)aniline)-3-[2,4-dioxo-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-1-yl) carbonyl] sulfonic acid (SPD6)- (scheme II A); 4-(2,5-dichloro-N-(2-phenoxyethyl)aniline)- 3-[2,4-dioxo-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-1-yl) carbonyl] sulfonic acid (SPD7) (scheme II A) and 4-(N-(2-phenoxyethyl)aniline)-3-[2,4-dioxo-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-1-yl) carbonyl] sulfonic acid (SPD3) (scheme II A) gives strong anti-convulsant effects against phenytoin drug.
Conclusion
The title compounds and their derivatives were examined for their ability to treat convulsions. Studies of the relationship between structure and activity revealed that compounds containing 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine derivatives that have an electron-withdrawing group have higher activity than those that have an electron-donating group.
Background
Chronic administration of D-galactose and aluminium chloride (D-gal/AlCl3) has been associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Delta- 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC) is the key psychoactive constituent in Cannabis sativa and has shown promising memory-enhancing capability. This study evaluated the therapeutic effects of Δ9THC on D-gal/AlCl3-induced AD-like rat models through behavioural and histological analysis.
Materials and Methods
Healthy male Wistar rats were subjected to AD induction by administering D-gal (60 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) and AlCl3 (200 mg/kg, oral) once daily for 10 consecutive weeks. Afterwards, Δ9THC (0.75 mg/kg, 1.5 mg/kg, and 3.0 mg/kg) were administered for 28 days as a treatment phase. Morris Water Maze (MWM) was employed to assess the rats’behaviour. The structural abnormalities in the hippocampus and neurogenesis markers were assessed.
Results
Treatment with Δ9THC alleviated the cognitive dysfunction, as recorded from the MWM, and restored the morphological aberrations in the rat’s hippocampus. Additionally, Δ9THC boosted neurogenesis by marked increased in GFAP+ cells, DCX+ cells, NeuN immunoreactivity and calbindin+ cells.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Δ9THC ameliorates D-gal/ AlCl3-induced AD-like cognitive deficits in rat models, which could be linked to its ability to enhance neurogenesis.

Background
This observational, prospective cross-sectional study aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of metoprolol and bisoprolol in the treatment of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) patients.
Materials and Methods
The study received institutional ethics approval and was conducted at a tertiary care private teaching hospital over six months. Ninety CAD patients were included, with demographics and clinical characteristics recorded. Vital signs were measured at baseline, 48 hr, 7 days, and 1 month. Angina severity was assessed using the Canadian Cardiovascular Society Grading Scale and New York Heart Association classification. Statistical analysis compared outcomes between metoprolol and bisoprolol groups.
Results
Male patients (72.22%) received metoprolol more frequently, while bisoprolol was preferred among females (28.88%). Age had minimal influence on medication choice. Metoprolol-treated patients had higher Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) values (50.26%) compared to bisoprolol-treated patients (45.78%). Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities (RWMA) was similar between groups. Both medications effectively reduced hypertension severity and vital parameters, with significant reductions in Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP), Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP), and Heart Rate (HR) with metoprolol. The prevalence of chest pain decreased in both groups, with Class III patients achieving complete relief. Breathlessness symptoms improved overall, with some patients experiencing relief while others showed reduced symptoms. Side effects were low in both groups, but metoprolol had a slightly higher incidence.
Conclusion
Metoprolol and bisoprolol demonstrated safety and efficacy in managing CAD patients. Metoprolol showed advantages in LVEF improvement and greater reduction in SBP, DBP, and HR, but it had a slightly higher side effect incidence. Both medications effectively alleviated chest pain and breathlessness symptoms. This study provides valuable insights into the clinical characteristics and outcomes associated with metoprolol and bisoprolol in CAD patients, supporting their use in managing cardiac symptoms and hypertension.

Background
Amid the pressing global concern of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), where Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) stands as a promising solution in relation to this, critical priority has been assigned to AMR pathogens in the Indian Pathogen Priority List to steer research focused on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The study’s particular objective is to assess how an AMS intervention affects these pathogens in adult patients.
Materials and Methods
Over a dedicated two-year period from January 2021 to November 2022 research focused on adult patients harboring critical priority pathogens, adhering to ICMR directives. The primary goal was to comprehend antimicrobial drug usage in hospital’s medicine and surgery unit. Employing a qualitative approach, study conducted a Prospective Audit with Feedback (PAF), implementing deliberate constraints on antimicrobial drug usage to gain insights.
Results
The analysis encompassed 314 participants: 96 in control phase, and 115 and 103 in the intervention phases 2 and 3. Comparable demographics and service scope existed between intervention and control groups. All arms exhibited the presence of culture-positive organisms from the critical priority pathogen list defined by ICMR. Impressively, length of therapy per 1000 patient days notably dropped from 908.50 to 758.33 (p=0.001) post-intervention.
Conclusion
The study’s conclusion highlights responsible antimicrobial use in a tertiary care setting, showcasing promising progress. Noteworthy impacts on the dependent variable (Log_LOT) emerged across study phases, emphasizing intervention significance. Statistically significant Ward and Phase variables further enriched the overall insights.
Background
Hypertension increases the risk of cerebrovascular illness and cognitive decline by directly affecting the cerebral artery vasomotor function causing premature death. As the retina and the brain have similar embryological origins, any microvascular alterations in the retina can detect subtle changes in the cerebral vasculature, which can be used to suspect the diagnosis of cerebral dysfunctions. The purpose of our study is to determine an association between Hypertensive Retinopathy (HTRP) and stroke.
Materials and Methods
This is a prospective observational study, 240 hypertensive patients were selected based on the inclusion criteria involving all age groups, Patients’ information was gathered using patient data collecting forms and the following were obtained: Demographic details, medical history, diagnosis and laboratory data was obtained. The data was sorted according to JNC-8 criteria and Keith-Wagner Classification for HTRP and entered into Microsoft excel and analyzed using SPSS software 26 version and the association was determined using Pearson chi-square and Pearson correlation.
Results
Out of 240 hypertensive patients 196 had stroke and 84 had HTRP. The association between HTRP and stroke was assessed in 40 individuals with both stroke and HTRP, A Pearson chi-square showed that there is a significant association between the two variables at 0.05 level [χ

Background
Liver diseases encompass a range of conditions that affect the normal functioning of the liver. They can result from various causes, including viral infections, excessive alcoholism, genetic factors, etc. These conditions can lead to symptoms like jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain, and in severe cases, they can pose life-threatening risks. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to mitigate the impact of liver diseases and improve patients’ quality of life. Hence, the present study is planned to investigate the prevalence, risk factors, and management of liver diseases in adults within a tertiary care teaching hospital.
Materials and Methods
A prospective case analysis study was conducted at the Department of General Medicine and Gastroenterology between October 2021 and March 2022. A total of 90 cases were included in the study. Data were collected on patient demographics, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnostic tests, and treatment modalities.
Results
Alcoholic liver disease was most prevalent (48%) liver disease, followed by viral hepatitis (22%) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (18%). Majority of patients were male (81%) and fell within the age group of 35 to 50 years (40%). Abdominal distention was the most common clinical complication (54%). Liver function tests and ultrasonography were the primary diagnostic tools. Ceftriaxone and Rifaximin were the most frequently prescribed medications.
Conclusion
Chronic alcoholism remains a major liver diseases contributor. This study emphasizes the importance of preventive measures against alcohol consumption and provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals managing liver diseases effectively.

Background
Vortioxetine had a positive effect on cognitive function and Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL), while fluoxetine produced conflicting effects. The effects of study drugs on HRQoL and cognitive function in Metabolic Syndrome (MS) patients are uncertain. This study examines the effect of vortioxetine and fluoxetine in cognition and HRQoL with and without MS.
Materials and Methods
Open-label, prospective, randomized controlled trial in the psychiatry department, patients were assigned either vortioxetine (group A) or fluoxetine (group B) and observed MS risk using International Diabetes Federation criteria, cognitive risk with the Saint Louis University Mental Status Examination score (SLUMS), and HRQoL using the RAND 36 questionnaire at baseline and at each visit (4,8,12,16,20 and 24 weeks).
Results
We examined 122 MDD patients, sixty in Group A (26 had MS and 34 were non-MS) and sixty-two in group B (32 had MS and 30 were non-MS). Groups A and B were compared using an independent sample t-test. According to SLUMS score group B exhibited mild cognitive impairment in comparison to group A in both MS and non-MS patients. The RAND 36 questionnaire found better HRQoL in group A than group B for MS, including physical function, role physical, emotional well-being, energy/fatigue, emotion well-being, social function, and general health. In non-MS patients, group A had better physical function and role physical than group B.
Conclusion
Vortioxetine shows greater potential as a therapeutic alternative for MDD patients with MS and cognitive function and improves HRQoL than fluoxetine.
Background
Cardiovascular disease often advances rapidly in people with diabetes mellitus, resulting in unfavorable clinical outcomes and complications after revascularization procedures. The purpose of our study was to determine how baseline parameters and Diabetes Mellitus (DM) affected clinical outcomes in the immediate aftermath of revascularization.
Materials and Methods
For this investigation, 189 patients who underwent CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Graft) and PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention) operations for revascularization during a five-month period in a South Indian tertiary care hospital were the subject of a hospital-based prospective observational analysis. During the first 30 days following revascularization, patients were assessed for clinical outcomes and baseline characteristics in the diabetic and non-diabetic groups. To ascertain the relevance of the findings, statistical analyses were carried out.
Results
The study reveals that there is no statistically significant difference in the type of surgery, number of grafts or stents, urgency of the surgery, angiographic finding, length of ventilation, volume of the chest drain, stay in the cardiothoracic unit, and length of hospitalization between the diabetes and non-diabetic cohorts. Arrhythmia, stroke after revascularization, re-exploration within discharge mortality, pulmonary embolism, hemorrhage, perioperative mortality, and postoperative mortality within 30 days were evaluated as follow-up events in both the groups and determined to be insignificant.
Conclusion
Even though prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is higher in diabetics, when comparing the diabetic and non-diabetic cohorts, it is not regarded as a risk factor for any negative outcomes following revascularization immediately within a period of thirty days following the angioplasty.

Background
Pharmaceutical care in 1990, they authored, “Pharmaceutical care is the responsible provision of drug therapy for the purpose of achieving definite outcome which improve patient quality of life” This study is to assess the knowledge, Attitude, Practice among Community Pharmacists for pharmaceutical care.
Materials and Methods
Self-prepared and validated questionanaires were distributed among Registered Community pharmacists in India through online forms from December 2022 to July 2023, a cross-sectional questionnaire-based survey was used, with convenience sampling utilised.
Results
The primary objective of this study was to assess the demographic details of the community pharmacist as well as the distribution of knowledge on pharmaceutical care services, community pharmacist’s attitude towards practice of pharmaceutical care, community pharmacist’s pharmaceutical care practices, barriers to implementation of pharmaceutical care. Among 350 community pharmacists’ male respondents are higher than female. Most of the community pharmacists have 1 to 5 years’ experience. Almost all respondents agrees that PC is mandatory for pharmacists. Most of the pharmacists provide counsel and advice during dispensing.
Conclusion
This study evaluated the knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of community pharmacists in India. According to the current survey, Community Pharmacists have fair knowledge but in practice, however, they are ineffective. In view of the above, steps must be taken to educate, empower, and train Community Pharmacists in the field of pharmaceutical care.
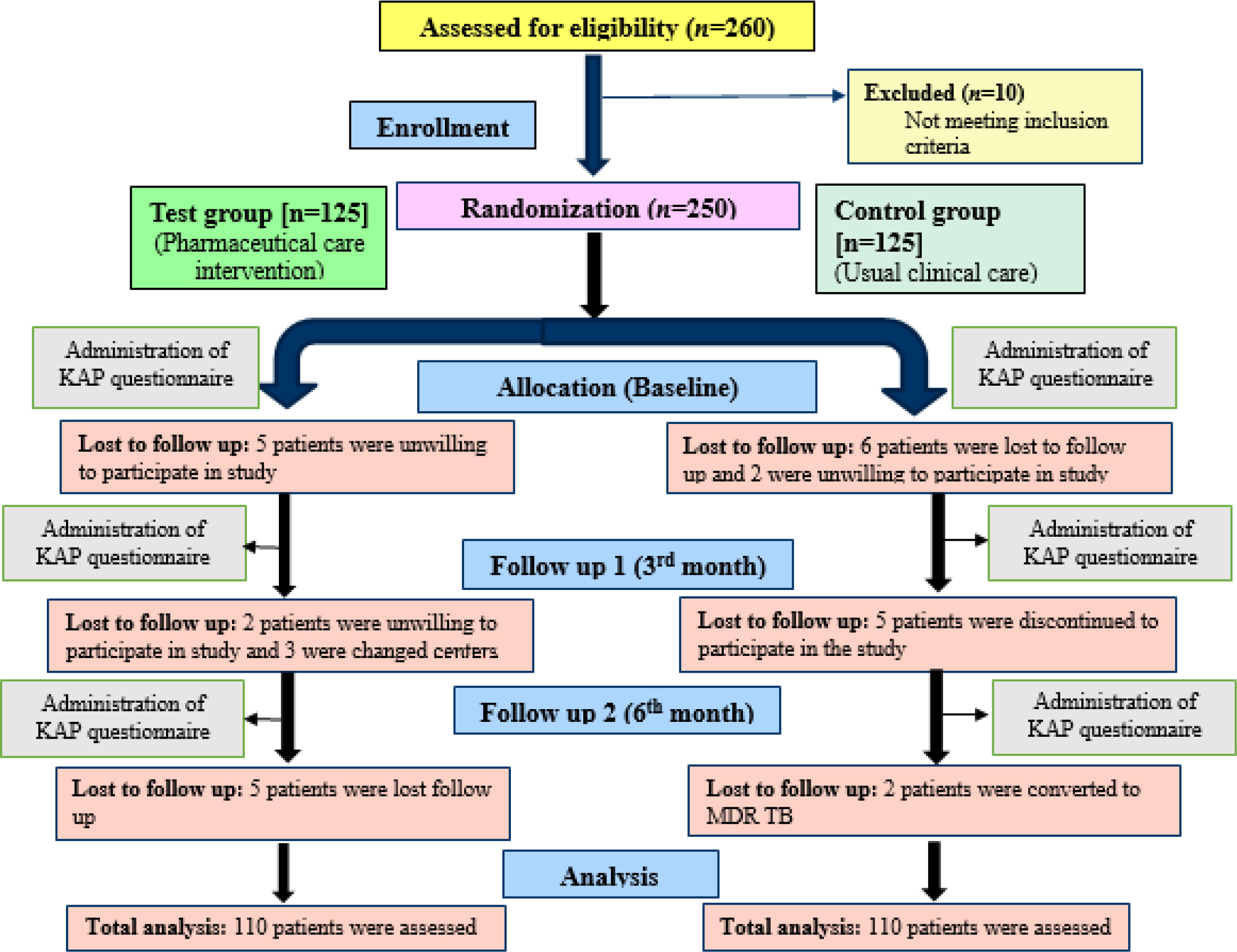
Background
India is among the highest burden of Tuberculosis (TB) cases across the world. Delaying the diagnosis and treatment adherence towards anti TB drugs were common causes observed among the TB patients. There is a need to identify the gaps and provide the awareness about the TB infection, which will help to achieve a ‘TB free India’ by 2025. Therefore, we aim to assess and evaluate the Knowledge, Attitude and Perception (KAP) among TB patients regarding the management of TB.
Materials and Methods
A Randomized controlled study was conducted among TB patients. A Self-prepared and validated KAP questionnaire was developed using World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations for TB KAP studies and interviewed the patients at the baseline. In test group by using patient information leaflets and counselling were given under the clinical pharmacist whereas in control group usual care was given by other health care team. Then two follow ups were done after every three months by using same set of questionnaires in both groups.
Results
A total of 250 participants were enrolled, among 220 were recruited in which majority of them belongs to 26-35 age group in both test 63 (57.27%) and control 66 (60%). In health seeking behaviour, most of them usually go to private clinic compared to government clinic or hospital. In response to TB knowledge and awareness, attitude with stigma and perception at baseline found to be low but at the end of sixth month the parameters were improved among both test and control group. The test group had shown better improved KAP than the control group.
Conclusion
Majority of the participants had inadequate levels of KAP at baseline but got improved in post follow ups among both test and control groups. Test group had shown more improvement compared to control group. Thus, indicating the importance of clinical pharmacist intervention in improving the KAP among TB patients.
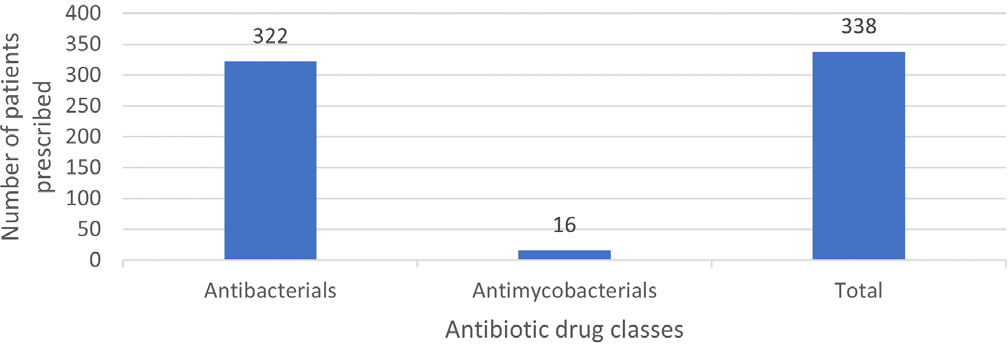
Background
Antibiotics are crucial for treating infections in older adults, but misuse can lead to drug-resistant bacteria, posing a global health challenge requiring urgent action. This study aimed to analyze the prescribing pattern of antibiotics among hospitalized older adults and identify factors influencing antibiotic use.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective cross-sectional study focused on older adults hospitalized at Thumbay University Hospital, Ajman, UAE, for a period of 12 months. Patients with a hospital stay over 24 hr, receiving at least one antibiotic, were included. Data were collected using a standardized tool from electronic medical records and analyzed using classifications like Charlson Comorbidity Index and various WHO classifications, including AWaRe and INRUD prescribing indicators.
Results
The study included 102 patients who received a total of 338 antibiotics. The most frequently prescribed class was systemic antibacterials, specifically cephalosporins and penems (41.25%). Piperacillin-tazobactam was the most used individual agent. High antibiotic prescribing rates related to skin and soft tissue infections (18.63%), pneumonia (18.04%), sepsis (17.75%), urinary tract infection (10.35%), and fracture and injury (8.57%). Patients generally received an average of 3.31 antibiotic agents. Most antibiotics prescribed were broad spectrum (81.95%), with 72.78% falling under the WHO AWaRe “Watch” group, indicating potential for resistance. Most antibiotics were from the national Essential Medicines List (82.24%) and prescribed using generic names (55.02%). The study also identified the total number of medications prescribed during hospital stay was found to correlate with the number of antibiotics prescribed.
Conclusion
The study unveiled a divergence from the WHO antibiotic prescribing guidelines. It recommends conducting large-scale surveillance studies along with instituting institutional and national guidelines to curb antibiotic misuse and overuse in tertiary care hospitals.
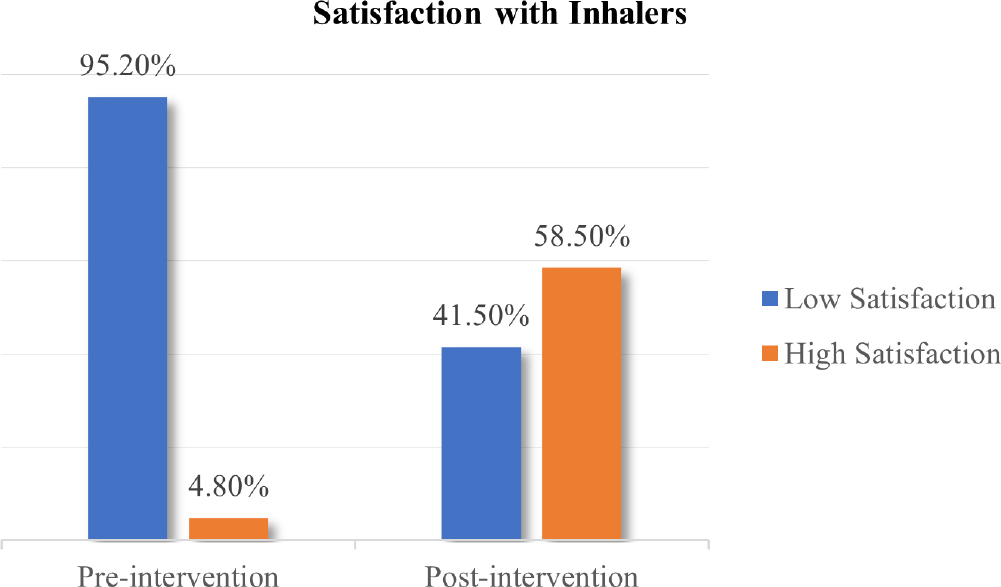
Background
Asthma is a rapidly increasing chronic respiratory disease worldwide. Inhalation drug therapy plays a vital role in asthma management because of immediate pharmacological response. Currently, a wide range of inhaler devices are being used worldwide, among which Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) are most commonly prescribed. Adherence with therapy directly depends upon the patient’s satisfaction with inhalation therapy. The current study aimed to determine the asthma patient’s satisfaction with inhalers. As well as the influence of pharmacist led educational intervention upon inhaler satisfaction of asthma patients.
Materials and Methods
The present cross-sectional study recruited 207 physician diagnosed adult asthmatics who were currently using MDI. The patient’s satisfaction with their inhaler was accessed through the study tool- FSI-10 questionnaire. After baseline observations, pharmacist led educational intervention was delivered to asthma patients. The pharmacist personally educated study subjects regarding the proper usage technique and importance of MDIs. Moreover, literature pamphlets containing inhaler technique were provided to patients at the end of intervention. Pre and post intervention satisfaction with inhaler was determined statistically.
Results
Majority of the asthma patients (197) i.e., 95.2% were observed to have low satisfaction regarding their pressurized meter dose inhalers. Only 4.8% patients presented high satisfaction with inhaler at baseline. However, patients’ satisfaction with their inhalers was raised from 4.8% to 58.5% as the result of intervention. The univariate analysis of the FSI-10 questionnaire data demonstrates a noteworthy association of the intervention given to patients regarding inhaler usage with its effect on the patients’ level of satisfaction with the inhaler. The current study showed p-value of 0.001 (p <0.05) which statistically proves that there is a significant effect of intervention on patients’ level of satisfaction with inhalers.
Conclusion
During baseline survey, majority of the patients presented poor satisfaction with their inhaler. But post intervention evaluation presented an enhancement in patient’s satisfaction with inhalers. Concluding that pharmacist led educational intervention proved to be effective in improving the patient’s satisfaction with inhalers.
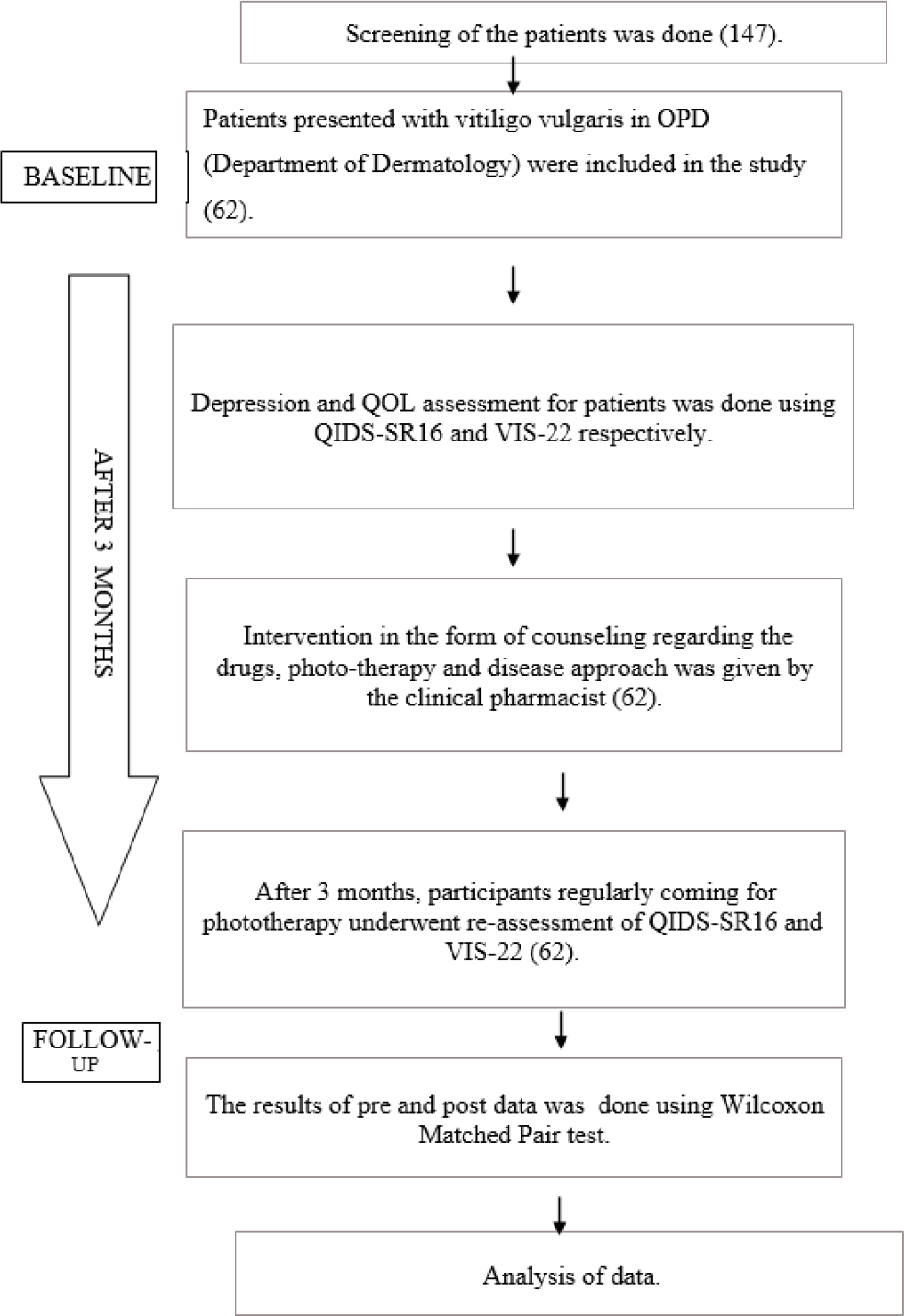
Background
Vitiligo vulgaris is an autoimmune de-pigmentary disorder characterized by skin depigmentation that can be localized or generalized, due to destructed melanocytes. It carries a majority of stigma and has a negative impact on patient’s psychological well-being. Hence, to determine the impact of clinical pharmacist intervention on depression levels and quality of life in vitiligo patients is of utmost importance.
Materials and Methods
A prospective study in Dept. of Dermatology at a tertiary care hospital was carried out after getting ethics committee approval. Vitiligo patients aged >18 years were included. The QIDS-SR16 (Quick Inventory Depression Symptomology-Self Rating Scale) and VIS-22 (Vitiligo Impact Scale-22) scales were used to determine depression level and quality of life, respectively.
Results
Among 62 patients enrolled in the study, 64.52% were female and 35.48% were male. At the baseline, the mean VIS-22 and QIDS-SR16 scores were 15.02 and 4.92 respectively. After the pre and post evaluation of VIS-22 and QIDS-SR16, a significant percentage of difference from the baseline data to the follow-up of approximately 40.64% in VIS-22 and 53.27% in QIDS SR16 was observed.
Conclusion
The findings of this study indicate that, in addition to pharmacological therapy, appropriate counseling and general education can aid in enhancing their psychosocial behavior and quality of life and help improve the negative stigmatization in society.

COVID-19 primarily impacts the respiratory system, with neurological manifestations often being thrombotic and affecting the nervous system. However, the specific presentation of demyelinating manifestations remains less clearly defined. While recent research has established a connection between COVID-19 and Guillain-Barré syndrome-a complex neurological disorder characterised by acute or chronic degeneration-the extent of this association and the distinctive features of GBS within this context remain uncertain. In this report, we present the case of acute GBS suspected to be induced by a COVID-19 infection. Notably, this patient did not exhibit any preceding respiratory, gastrointestinal, or systemic illnesses. Consequently, this case underlines the critical importance of acknowledging the potential risk of Guillain-Barré Syndrome following a COVID-19 infection, making a significant contribution to raising awareness about this potential association.

Bladder Exstrophy is an anomaly that is uncommon from birth and influences various aspects of the urinary tract, genitals, pelvis, and anus. The defining characteristic of this condition is the abnormal development of the bladder outside the fetal body. Clinical signs in affected individuals often include the bladder being exposed from the abdomen, a flattened puborectalis sling, separation of the pubic symphysis, and ulcers in the bladder mucosa, urine dribbling, and skin excoriation. The primary treatment for bladder exstrophy typically involves surgery, tailored to the severity of the condition. In one case, a female child was passing urine through her navel instead of the urethra. Following a confirmed diagnosis, a single-stage repair was recommended for the exstrophied bladder. However, before a scheduled follow-up appointment, the patient’s stitches ruptured, resulting in urine leakage from the operated site and pus discharge from the urethra. Based on the patient’s complaints and laboratory results, a diagnosis of acute kidney injury and urinary tract infection in the context of bladder exstrophy was established, leading to the plan for a resuturing surgery. It’s important to note that the risk of bladder exstrophy is increased when the mother is exposed to smoking and radiation during the first trimester of pregnancy. Bladder exstrophy in a female child is a rare and complex congenital condition that necessitates a multidisciplinary approach for diagnosis, management, and long-term care.

This case report presents the challenging clinical scenario of a middle-aged male patient with a decade-long history of psychiatric illness on chronic neuroleptic therapy. The patient’s symptoms initially manifested as tremors a year ago, subsequently progressing to resting tremors, head titubation, and impaired mobility. Typically, Drug-Induced Parkinsonism (DIP) occurs within three months of initiating neuroleptic treatment, this case presents a unique and prolonged timeline, raising questions about the underlying aetiology complexed with patients’ imaging studies revealing age related atrophy. The bilateral and symmetrical motor signs observed align with DIP characteristics, although studies report asymmetrical signs, introducing diagnostic complexities. This case emphasizes the need for further research on understanding the effect of chronic neuroleptic use, age-related structural alterations, and the potential unmasking of underlying Parkinsonism for improving diagnostic accuracy and tailoring effective management strategies for patients with similar challenging presentations.

